0x00 前言
Windows 从 vista 版本引入一种进程保护机制(Process Protection),用于更进一步的控制进程的访问级别,在此之前,用户只需要使用 SeDebugPrivilege 令牌权限即可获取任意进程的所有访问权限;随后 Windows8.1 在此进程保护的基础上,扩展引入了进程保护光机制(Protected Process Light),简称 PPL 机制,其能提供更加细粒度化的进程访问权限控制,。
本文将介绍 Windows 的 PPL 安全机制,以及在实验环境下如何绕过该机制,从而实现对 PPL 的进程进行动态调试。
本文实验环境:
Windows 10 专业版 22H2
Visual Studio 20190x01 PPL机制
使用 Process Explorer 工具查看进程列表,我们可以看到 Windows 的部分核心进程设置了 PPL 保护:

对于安全研究来说,PPL机制最直观的感受就是即便使用管理员权限也无法 attach 这个进程进行调试:

通过官网文档(https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/procthread/zwqueryinformationprocess)可以了解到 PS_PROTECTION 的结构如下:
typedef struct _PS_PROTECTION {
union {
UCHAR Level;
struct {
UCHAR Type : 3;
UCHAR Audit : 1; // Reserved
UCHAR Signer : 4;
};
};
} PS_PROTECTION, *PPS_PROTECTION;前 3 位包含进程保护的类型:
typedef enum _PS_PROTECTED_TYPE {
PsProtectedTypeNone = 0,
PsProtectedTypeProtectedLight = 1,
PsProtectedTypeProtected = 2
} PS_PROTECTED_TYPE, *PPS_PROTECTED_TYPE;后 4 位包含进程保护的签名者标识:
typedef enum _PS_PROTECTED_SIGNER {
PsProtectedSignerNone = 0,
PsProtectedSignerAuthenticode,
PsProtectedSignerCodeGen,
PsProtectedSignerAntimalware,
PsProtectedSignerLsa,
PsProtectedSignerWindows,
PsProtectedSignerWinTcb,
PsProtectedSignerWinSystem,
PsProtectedSignerApp,
PsProtectedSignerMax
} PS_PROTECTED_SIGNER, *PPS_PROTECTED_SIGNER;通过 WinDBG 进行本地内核调试,查看上图进程 smss.exe(412) 的内核对象 EPROCESS 可以查看 PPL=0x61,如下:

PPL 机制在内核函数 NtOpenProcess 进行实现,当我们访问进程时最终都会调用该函数;NtOpenProcess 位于 ntoskrnl.exe 内,结合符号表逆向如下:

经过一系列的调用,最终进入到 PPL 检查的关键逻辑 RtlTestProtectedAccess,其调用栈如下:

RtlTestProtectedAccess 的判断逻辑如下:

其中 Protection.Signer 经过 RtlProtectedAccess 转换的权限如下:
PsProtectedSignerNone 0 => 0x0
PsProtectedSignerAuthenticode 1 => 0x2
PsProtectedSignerCodeGen 2 => 0x4
PsProtectedSignerAntimalware 3 => 0x108
PsProtectedSignerLsa 4 => 0x110
PsProtectedSignerWindows 5 => 0x13e
PsProtectedSignerWinTcb 6 => 0x17e
PsProtectedSignerWinSystem 7 => 0x1fe
PsProtectedSignerApp 8 => 0x0实际
NtOpenProcess中还有诸多条件影响 PPL 的检查,不过本文我们主要关注核心判断逻辑RtlTestProtectedAccess就可以了。
0x02 双机调试bypass
使用双机内核调试可以无视大多数的安全机制,这里我使用网络双机调试,成功连接被调试主机后,再进入到有 PPL 机制的 smss.exe(412) 的进程空间下,直接就可以正常调试: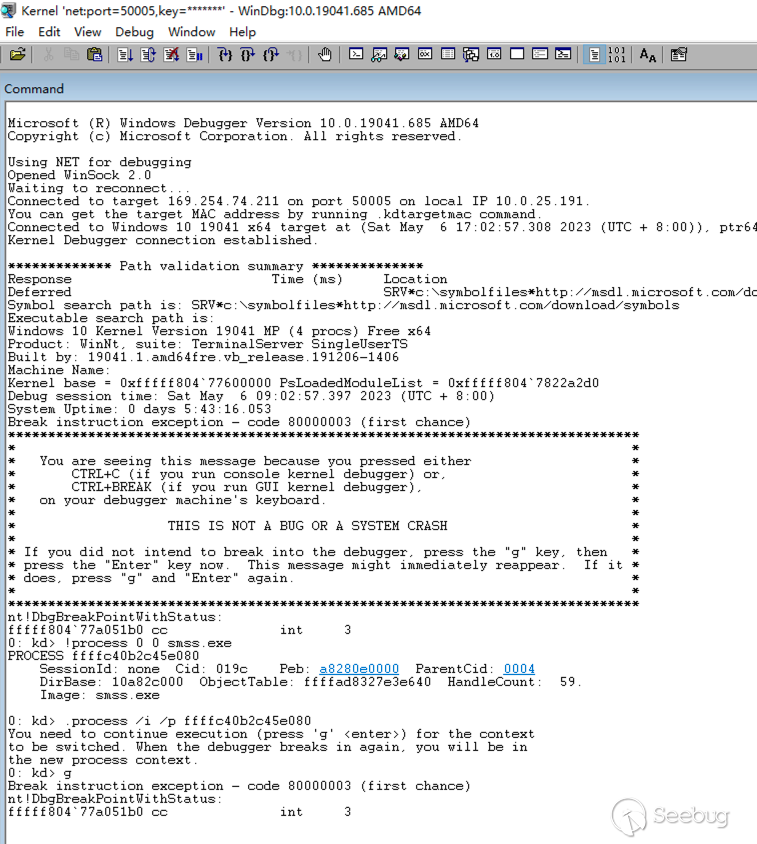
但是实际场景下双机调试可能受环境限制,同时双机调试也不如用户模式下方便,下面我们看看通过本地调试的方法来绕过 PPL 机制。
0x03 本地调试bypass
通过上文对 PPL 机制的介绍,我们知道 PPL 的标识位是以 _PS_PROTECTION 结构存放于 EPROCESS 进程对象中,虽然本地内核调试无法控制程序执行流,但可以修改内存值;那么我们可以先通过本地内核调试去除 PPL 标识,随后便可以在用户模式下调试目标进程。
配置好本地内核调试环境后,使用管理员权限启动 WinDBG,覆写 smss.exe(412) 进程的 Protection = 0x00 命令如下:
# 获取 smss.exe 进程的 EPROCESS 地址
lkd > !process 0 0 smss.exe
# 从 EPROCESS 获取 Protection 的偏移和值
lkd > dt nt!_eprocess ffffc40b2c45e080 Protection
lkd > db ffffc40b2c45e080+0x87a l1
# 将 Protection 值修改为 0x00
lkd > eb ffffc40b2c45e080+0x87a 0x00执行如下: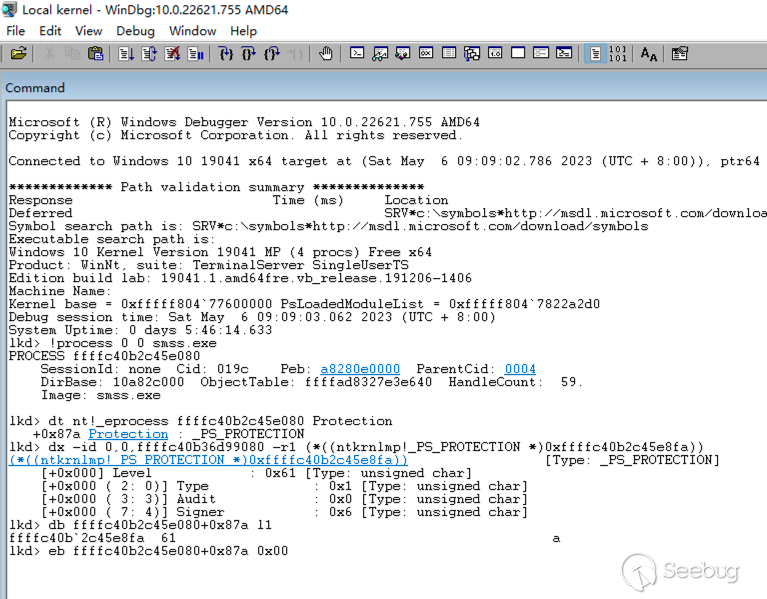
随后我们再以管理员权限启动 WinDBG,attach 到目标进程上,可以成功进行调试: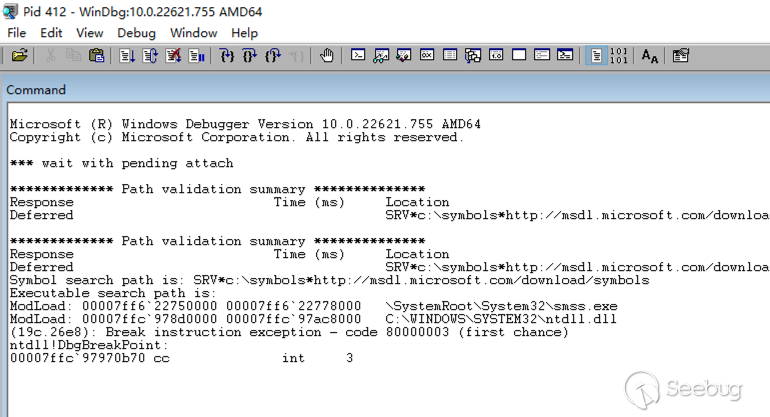
0x04 工具化
根据本地内核调试去除 PPL 标识的思路,我们可以编写驱动程序如下,使用 ZwQuerySystemInformation() 遍历进程,使用 PsLookupProcessByProcessId() 获取进程的 EPROCESS,随后按 Protection 的偏移将其内存值覆写为 0x00:
#include <ntifs.h>
#include <wdf.h>
#define EPROCESS_PROTECTION_OFFSET 0x87A // windows10 professional 22H2
DRIVER_INITIALIZE DriverEntry;
typedef enum _SYSTEM_INFORMATION_CLASS {
SystemProcessInformation = 5,
// ...
} SYSTEM_INFORMATION_CLASS;
typedef struct _SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION {
ULONG NextEntryOffset;
ULONG NumberOfThreads;
BYTE Reserved1[48];
PVOID Reserved2[3];
HANDLE UniqueProcessId;
PVOID Reserved3;
ULONG HandleCount;
BYTE Reserved4[4];
PVOID Reserved5[11];
SIZE_T PeakPagefileUsage;
SIZE_T PrivatePageCount;
LARGE_INTEGER Reserved6[6];
} SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION, *PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION;
NTSTATUS NTAPI ZwQuerySystemInformation(
_In_ SYSTEM_INFORMATION_CLASS SystemInformationClass,
_Inout_ PVOID SystemInformation,
_In_ ULONG SystemInformationLength,
_Out_opt_ PULONG ReturnLength
);
NTKERNELAPI UCHAR* PsGetProcessImageFileName(__in PEPROCESS Process);
VOID OnUnload(_In_ PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(DriverObject);
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: unload driver\n"));
}
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(_In_ PDRIVER_OBJECT DriverObject, _In_ PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath) {
ULONG BufferSize = 0;
NTSTATUS Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
PVOID Buffer = NULL;
PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION pInfo = NULL;
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(DriverObject);
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(RegistryPath);
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: driver entry\n"));
// register unload function
DriverObject->DriverUnload = OnUnload;
// get size of SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION
Status = ZwQuerySystemInformation(SystemProcessInformation, NULL, 0, &BufferSize);
if (Status != STATUS_INFO_LENGTH_MISMATCH) {
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: ZwQuerySystemInformation get size failed status=0x%x\n", Status));
goto _LABEL_EXIT;
}
// alloc memory and get SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION
Buffer = ExAllocatePoolWithTag(PagedPool, BufferSize, '1gaT');
if (Buffer == NULL) {
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: ExAllocatePoolWithTag failed\n"));
goto _LABEL_EXIT;
}
Status = ZwQuerySystemInformation(SystemProcessInformation, Buffer, BufferSize, &BufferSize);
if (Status != STATUS_SUCCESS) {
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: ZwQuerySystemInformation get info failed status=0x%x\n", Status));
goto _LABEL_EXIT;
}
// traverse all processes and rewrite "Protection" to 0x00
pInfo = (PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION)Buffer;
do {
PEPROCESS Process = NULL;
Status = PsLookupProcessByProcessId(pInfo->UniqueProcessId, &Process);
if (NT_SUCCESS(Status)) {
BYTE* Protection = (BYTE*)Process + EPROCESS_PROTECTION_OFFSET;
if (*Protection != 0) {
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: rewrite %s[%d] Protection=0x%x to 0x00\n",
PsGetProcessImageFileName(Process), pInfo->UniqueProcessId, *Protection));
*Protection = 0x00;
}
}
else {
KdPrintEx((DPFLTR_IHVDRIVER_ID, DPFLTR_INFO_LEVEL, "remove_ppl: PsLookupProcessByProcessId [%d] failed status=0x%x\n",
pInfo->UniqueProcessId, Status));
}
pInfo = (PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION)((PUCHAR)pInfo + pInfo->NextEntryOffset);
} while (pInfo->NextEntryOffset);
_LABEL_EXIT:
if (Buffer != NULL) {
ExFreePoolWithTag(Buffer, '1gaT');
}
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}成功编译后,将驱动程序注册为服务来启动运行(需设置主机为测试模式):
# 注册驱动程序为服务
sc.exe create remove_ppl type= kernel start= demand binPath= [src]remove_ppl.sys
# 查看服务信息
sc.exe queryex remove_ppl
# 启动驱动程序/服务
sc.exe start remove_ppl运行驱动程序,并使用 Process Explorer 查看,所有进程的 PPL 标识都被去除了:

除了以上实验代码外,也可以参考更加完善的 PPL 控制工具:
0x0x References
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/services/protecting-anti-malware-services-
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/procthread/zwqueryinformationprocess
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/procthread/process-security-and-access-rights
https://download.microsoft.com/download/a/f/7/af7777e5-7dcd-4800-8a0a-b18336565f5b/process_vista.doc
https://www.crowdstrike.com/blog/evolution-protected-processes-part-1-pass-hash-mitigations-windows-81/
https://www.crowdstrike.com/blog/evolution-protected-processes-part-2-exploitjailbreak-mitigations-unkillable-processes-and/
https://www.cnblogs.com/H4ck3R-XiX/p/15872255.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/revercc/p/16961961.html
https://itm4n.github.io/debugging-protected-processes/
https://paper.seebug.org/1892/
https://github.com/Mattiwatti/PPLKiller
https://github.com/itm4n/PPLcontrol
原文始发于0x7F@知道创宇404实验室:Windows 的 PPL 安全机制和绕过