原文始发于inversecos:How to Perform Clipboard Forensics: ActivitiesCache.db, Memory Forensics and Clipboard History
How to Perform Clipboard Forensics: ActivitiesCache.db, Memory Forensics and Clipboard History
During a compromise, threat actors often copy-paste data to the clipboard – usually credentials, PowerShell commands or IPs. When it comes to malware, infostealers, RATs and keyloggers often monitor what is being stored in the clipboard (as it may contain cryptocurrency seed phrases, passwords, and interesting data).
Incident response analysts also rarely perform forensic examination of clipboard data due to the transient nature of the data residing in volatile memory and setting prerequisites. However, with the advent of the latest Windows updates, depending on how the system is configured – historical clipboard data may be stored on the system for analysis. This should be considered the next time an analyst is performing forensic analysis of a system.
Forensic considerations when analysing clipboard data:
- What time did the threat actor copy data to the clipboard?
- Where did the threat actor copy data to the clipboard from?
- Was the data ever pasted (on the same system) or just copied?
Scenarios when clipboard forensics is necessary:
To demonstrate the importance of analysing clipboard artefacts – here are some real-life examples where knowing the clipboard data may have helped an engagement:
- Signs of RDPCLIP.exe being executed as it supports the use of clipboard during RDP sessions
- Ransomware engagements where AnyDesk and TeamViewer logs reference clipboard data
- Malware (typically RATs, infostealers or keyloggers) leveraged by commodity groups and APT groups that hooks into API calls like OpenClipboard() and GetClipboardData().
- Other incident response engagements where threat actors may be coping credentials / commands during sessions
This blog post explores three methods to forensically examine clipboard data – the first method being an artefact on disk, the second through forensic examination of RAM and the third being a folder that’s resident on disk which stores data.
Detection Method 1: ActivitiesCache.db
The artefact ActivitiesCache.db has started to log clipboard activity since Windows 10 version 1803. (If you are not familiar with this artefact it is immensely useful during an investigation as it tracks several things like program execution. It will even tell you down to the detail where a program i.e. notepad.exe was used to open a file called “file.txt”).
If you’re interested in reading more about ActivitesCache.db I recommend you check out the following blog posts and write-ups:
- Costas: https://kacos2000.github.io/WindowsTimeline/WindowsTimeline.pdf
- Cellebrite: https://cellebrite.com/en/exploring-the-windows-activity-timeline-part-3-the-value-of-clipboard-content/?utm_content=134912769&utm_medium=social&utm_source=twitter&hss_channel=tw-209890844
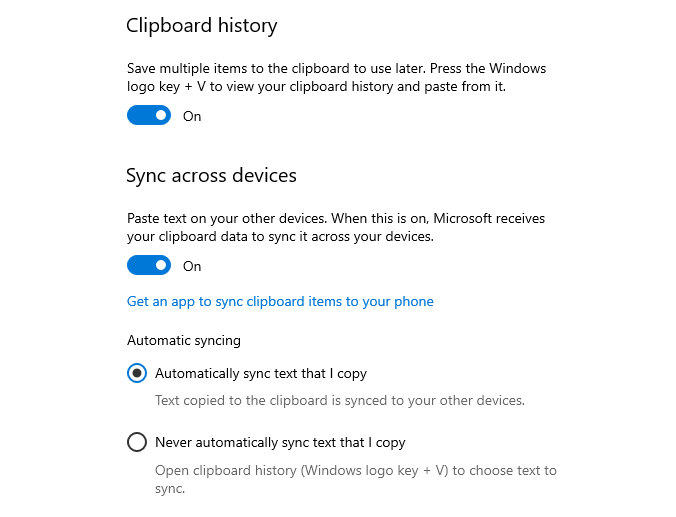
Step 1: Check the system has clipboard history and sync enabled
The prerequisite for clipboard data to be logged by this artefact relies on the system having two settings checked:
- Clipboard history enabled
- Clipboard sync across devices
A screenshot of this can be seen below:
Step 2: Locate the database file for analysis
- ActivitiesCache.db (the database file that we can analyse)
- ActivitiesCache.db-shm
- ActivitiesCache.db-wal (the write-ahead log which can also be analysed for data)

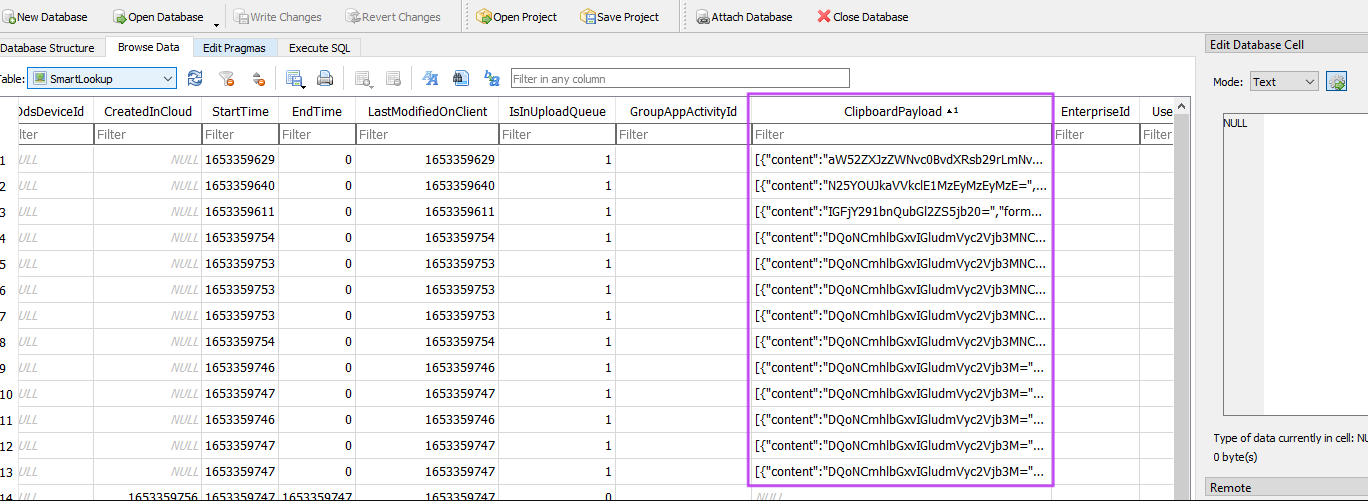
- StartTime (epoch time) – When the data was first copied to the clipboard
- ExpirationTime (epoch time) – When the data will be deleted from the ActivitiesCache.db (roughly 12 hours)
- ClipboardPayload – Base64 encoded string of the clipboard contents
- Payload – This field tells you where the clipboard data was copied from!
- ActivityType – Type 10 means data resides in clipboard, Type 16 shows if data was copied or pasted

Step 3: Look for any entries showing clipboard activity


Step 5: Determine what was copied into the clipboard

Step 6: Determine if the data was ever pasted back onto the system

Detection Method 2: Memory Forensics

- Pinned
- HistoryData
- Clipboard history will only store clipboard text that is under 4MB per text
- Clipboard history will also save HTML and bitmaps (not just text) whereas the ActivitiesCache.db only stores text format
- Clipboard history will only store 25 entries
- Clipboard history is cleared whenever you restart the system
转载请注明:How to Perform Clipboard Forensics: ActivitiesCache.db, Memory Forensics and Clipboard History | CTF导航